Phosphorylation and desensitization of the lysophosphatidic acid receptor LPA1
- PMID: 15369458
- PMCID: PMC1134742
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20040891
Phosphorylation and desensitization of the lysophosphatidic acid receptor LPA1
Abstract
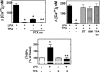
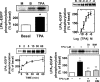
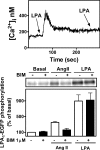
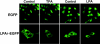
In C9 cells, LPA (lysophosphatidic acid) induced inositol phosphate production, increased intracellular calcium concentration and inhibited adenylate cyclase activity. These responses were abolished in cells challenged with active phorbol esters. Action of phorbol esters was blocked by inhibitors of PKC (protein kinase C) and by its down-regulation. LPA1 receptor phosphorylation was observed in response to phorbol esters. The effect was rapid (t1/2 approximately 1 min), intense (2-fold) and sustained (at least 60 min). PKC inhibitors markedly decreased the LPA1 receptor phosphorylation induced by phorbol esters. LPA1 receptor tagged with the green fluorescent protein internalized in response to PKC activation. In addition, LPA and angiotensin II were also capable of inducing LPA1 receptor phosphorylation, showing that LPA1 receptor can be subjected to homologous and heterologous desensitization.
Figures



References
-
- van Corven E. J., Groenink A., Jalink K., Eichholtz T., Moolenaar W. H. Lysophosphatidate-induced cell proliferation: identification and dissection of signaling pathways mediated by G proteins. Cell (Cambridge, Mass.) 1989;59:45–54. - PubMed
-
- Moolenaar W. H. Mitogenic action of lysophosphatidic acid. Adv. Cancer Res. 1991;57:87–102. - PubMed
-
- Lummen G., Virchow S., Rumenapp U., Schmidt M., Wieland T., Otto T., Rubben H., Jakobs K. H. Identification of G protein-coupled receptors potently stimulating migration of human transitional-cell carcinoma cells. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 1997;356:769–776. - PubMed
-
- Lynch K. R., Im D. S. Life on the edg. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 1999;20:473–475. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

