Identification of a novel telomerase repressor that interacts with the human papillomavirus type-16 E6/E6-AP complex
- PMID: 15371341
- PMCID: PMC517520
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1214704
Identification of a novel telomerase repressor that interacts with the human papillomavirus type-16 E6/E6-AP complex
Abstract
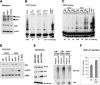
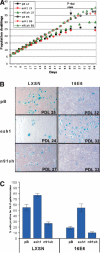
The critical immortalizing activity of the human papillomavirus (HPV) type-16 E6 oncoprotein is to induce expression of hTERT, the catalytic and rate-limiting subunit of telomerase. Additionally, E6 binds to a cellular protein called E6-associated protein (E6-AP) to form an E3 ubiquitin ligase that targets p53 for proteasome-dependent degradation. Although telomerase induction and p53 degradation are separable and distinct functions of E6, binding of E6 to E6-AP strongly correlated with the induction of hTERT. Here, we demonstrate using shRNAs to reduce E6-AP expression that E6-AP is required for E6-mediated telomerase induction. A yeast two-hybrid screen to find new targets of the E6/E6-AP E3 ubiquitin ligase complex identified NFX1. Two isoforms of NFX1 were found: NFX1-123, which coactivated with c-Myc at the hTERT promoter, and NFX1-91, which repressed the hTERT promoter. NFX1-91 was highly ubiquitinated and destabilized in epithelial cells expressing E6. Furthermore, knockdown of NFX1-91 by shRNA resulted in derepression of the endogenous hTERT promoter and elevated levels of telomerase activity. We propose that the induction of telomerase by the HPV-16 E6/E6-AP complex involves targeting of NFX1-91, a newly identified repressor of telomerase, for ubiquitination and degradation.
Figures

References
-
- Baege A.C., Berger, A., Schlegel, R., Veldman, T., and Schlegel, R. 2002. Cervical epithelial cells transduced with the papillomavirus E6/E7 oncogenes maintain stable levels of oncoprotein expression but exhibit progressive, major increases in hTERT gene expression and telomerase activity. Am. J. Pathol. 160: 1251-1257. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bartz S.R. and Vodicka, M.A. 1997. Production of high-titer human immunodeficiency virus type 1 pseudotyped with vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein. Methods 12: 337-342. - PubMed
-
- Boyer S.N., Wazer, D.E., and Band, V. 1996. E7 protein of human papilloma virus-16 induces degradation of retinoblastoma protein through the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. Cancer Res. 56: 4620-4624. - PubMed
-
- Chong S.R., Mersha, F.B., Comb, D.G., Scott, M.E., Landry, D., Vence, L.M., Perler, F.B., Benner, J., Kucera, R.B., Hirvonen, C.A., et al. 1997. Single-column purification of free recombinant proteins using a self-cleavable affinity tag derived from a protein splicing element. Gene 192: 271-281. - PubMed
-
- Cong Y.S. and Bacchetti, S. 2000. Histone deacetylation is involved in the transcriptional repression of hTERT in normal human cells. J. Biol. Chem. 275: 35665-35668. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
