Core promoter sequences contribute to ovo-B regulation in the Drosophila melanogaster germline
- PMID: 15371353
- PMCID: PMC1350745
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.104.033118
Core promoter sequences contribute to ovo-B regulation in the Drosophila melanogaster germline
Abstract
Utilization of tightly linked ovo-A vs. ovo-B germline promoters results in the expression of OVO-A and OVO-B, C(2)H(2) transcription factors with different N -termini, and different effects on target gene transcription and on female germline development. We show that two sex-determination signals, the X chromosome number within the germ cells and a female soma, differentially regulate ovo-B and ovo-A. We have previously shown that OVO regulates ovarian tumor transcription by binding the transcription start site. We have explored the regulation of the ovo-B promoter using an extensive series of transgenic reporter gene constructs to delimit cis-regulatory sequences as assayed in wild-type and sex-transformed flies and flies with altered ovo dose. Minimum regulated expression of ovo-B requires a short region flanking the transcription start site, suggesting that the ovo-B core promoter bears regulatory information in addition to a "basal" activity. In support of this idea, the core promoter region binds distinct factors in ovary and testis extracts, but not in soma extracts, suggesting that regulatory complexes form at the start site. This idea is further supported by the evolutionarily conserved organization of OVO binding sites at or near the start sites of ovo loci in other flies.
Figures





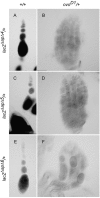

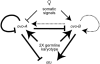
Similar articles
-
Sex determination signals control ovo-B transcription in Drosophila melanogaster germ cells.Genetics. 2002 Feb;160(2):537-45. doi: 10.1093/genetics/160.2.537. Genetics. 2002. PMID: 11861560 Free PMC article.
-
Drosophila OVO regulates ovarian tumor transcription by binding unusually near the transcription start site.Development. 2001 May;128(9):1671-86. doi: 10.1242/dev.128.9.1671. Development. 2001. PMID: 11290304
-
Regulatory and functional interactions between ovarian tumor and ovo during Drosophila oogenesis.Mech Dev. 1999 Oct;88(1):3-14. doi: 10.1016/s0925-4773(99)00167-7. Mech Dev. 1999. PMID: 10525184
-
Sex determination of germ cells in Drosophila.Ciba Found Symp. 1994;182:193-202; discussion 202-9. doi: 10.1002/9780470514573.ch11. Ciba Found Symp. 1994. PMID: 7835150 Review.
-
Germ cell sex determination: a collaboration between soma and germline.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2010 Dec;22(6):722-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2010.09.006. Epub 2010 Oct 26. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 21030233 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Global analysis of X-chromosome dosage compensation.J Biol. 2006;5(1):3. doi: 10.1186/jbiol30. Epub 2006 Feb 16. J Biol. 2006. PMID: 16507155 Free PMC article.
-
A truncated form of a transcription factor Mamo activates vasa in Drosophila embryos.Commun Biol. 2019 Nov 20;2:422. doi: 10.1038/s42003-019-0663-4. eCollection 2019. Commun Biol. 2019. PMID: 31799425 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide computational prediction and analysis of core promoter elements across plant monocots and dicots.PLoS One. 2013 Oct 29;8(10):e79011. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0079011. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24205361 Free PMC article.
-
Drosophila germline sex determination: integration of germline autonomous cues and somatic signals.Curr Top Dev Biol. 2008;83:109-50. doi: 10.1016/S0070-2153(08)00404-3. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2008. PMID: 19118665 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative genomics of Drosophila and human core promoters.Genome Biol. 2006;7(7):R53. doi: 10.1186/gb-2006-7-7-r53. Genome Biol. 2006. PMID: 16827941 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Altschul, S. F., W. Gish, W. Miller, E. W. Myers and D. J. Lipman, 1990. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 215: 403–410. - PubMed
-
- Andrews, J., I. Levenson and B. Oliver, 1998. New AUG initiation codons in a long 5′ UTR create four dominant negative alleles of the Drosophila C2H2 zinc-finger gene ovo. Dev. Genes Evol. 207: 482–487. - PubMed
-
- Andrews, J., D. Garcia-Estefania, I. Delon, J. Lu, M. Mevel-Ninio et al., 2000. OVO transcription factors function antagonistically in the Drosophila female germline. Development 127: 881–892. - PubMed
-
- Arnosti, D. N., 2003. Analysis and function of transcriptional regulatory elements: insights from Drosophila. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 48: 579–602. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

