The Caenorhabditis elegans Ror RTK CAM-1 inhibits EGL-20/Wnt signaling in cell migration
- PMID: 15371357
- PMCID: PMC1448710
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.104.031781
The Caenorhabditis elegans Ror RTK CAM-1 inhibits EGL-20/Wnt signaling in cell migration
Abstract
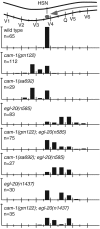
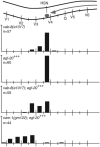
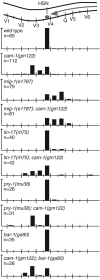
During Caenorhabditis elegans development, the HSN neurons and the right Q neuroblast and its descendants undergo long-range anteriorly directed migrations. Both of these migrations require EGL-20, a C. elegans Wnt homolog. Through a canonical Wnt signaling pathway, EGL-20/Wnt transcriptionally activates the Hox gene mab-5 in the left Q neuroblast and its descendants, causing the cells to migrate posteriorly. In this report, we show that CAM-1, a Ror receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) family member, inhibits EGL-20 signaling. Excess EGL-20, like loss of cam-1, caused the HSNs to migrate too far anteriorly. Excess CAM-1, like loss of egl-20, shifted the final positions of the HSNs posteriorly and caused the left Q neuroblast descendants to migrate anteriorly. The reversal in the migration of the left Q neuroblast and its descendants resulted from a failure to express mab-5, an egl-20 mutant phenotype. Our data suggest that CAM-1 negatively regulates EGL-20.
Figures




References
-
- Afzal, A. R., A. Rajab, C. D. Fenske, M. Oldridge, N. Elanko et al., 2000. Recessive Robinow syndrome, allelic to dominant brachydactyly type B, is caused by mutation of ROR2. Nat. Genet. 25: 419–422. - PubMed
-
- Al-Shawi, R., S. V. Ashton, C. Underwood and J. P. Simons, 2001. Expression of the Ror1 and Ror2 receptor tyrosine kinase genes during mouse development. Dev. Genes Evol. 211: 161–171. - PubMed
-
- Bhanot, P., M. Brink, C. H. Samos, J. C. Hsieh, Y. Wang et al., 1996. A new member of the frizzled family from Drosophila functions as a Wingless receptor. Nature 382: 225–230. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

