Decreased susceptibility to renovascular hypertension in mice lacking the prostaglandin I2 receptor IP
- PMID: 15372104
- PMCID: PMC516260
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI21382
Decreased susceptibility to renovascular hypertension in mice lacking the prostaglandin I2 receptor IP
Abstract
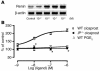
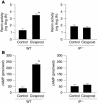
Persistent reduction of renal perfusion pressure induces renovascular hypertension by activating the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system; however, the sensing mechanism remains elusive. Here we investigated the role of PGI2 in renovascular hypertension in vivo, employing mice lacking the PGI2 receptor (IP-/- mice). In WT mice with a two-kidney, one-clip model of renovascular hypertension, the BP was significantly elevated. The increase in BP in IP-/- mice, however, was significantly lower than that in WT mice. Similarly, the increases in plasma renin activity, renal renin mRNA, and plasma aldosterone in response to renal artery stenosis were all significantly lower in IP-/- mice than in WT mice. All these parameters were measured in mice lacking the four PGE2 receptor subtypes individually, and we found that these mice had similar responses to WT mice. PGI2 is produced by COX-2 and a selective inhibitor of this enzyme, SC-58125, also significantly reduced the increases in plasma renin activity and renin mRNA expression in WT mice with renal artery stenosis, but these effects were absent in IP-/- mice. When the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system was activated by salt depletion, SC-58125 blunted the response in WT mice but not in IP-/- mice. These results indicate that PGI2 derived from COX-2 plays a critical role in regulating the release of renin and consequently renovascular hypertension in vivo.
Figures
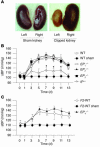
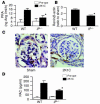
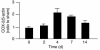
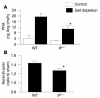
Comment in
-
Prostanoids and blood pressure: which way is up?J Clin Invest. 2004 Sep;114(6):757-9. doi: 10.1172/JCI22929. J Clin Invest. 2004. PMID: 15372097 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pickering, T.G., and Laragh, J.H. 1991. Renovascular hypertension. In The kidney. B.M. Brenner and F.C. Rector, Jr., editors. W.B. Saunders Co. Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, USA. 1940–1967.
-
- Hartner A, Goppelt-Struebe M, Hilgers KF. Coordinate expression of cyclooxygenase-2 and renin in the rat kidney in renovascular hypertension. Hypertension. 1998;31:201–205. - PubMed
-
- Harris RC, Breyer MD. Physiological regulation of cyclooxygenase-2 in the kidney. Am. J. Physiol. 2001;281:F1–F11. - PubMed
-
- Imanishi M, Tsuji T, Nakamura S, Takamiya M. Prostaglandin I2/E2 ratios in unilateral renovascular hypertension of different severities. Hypertension. 2001;38:23–29. - PubMed
-
- Jackson EK, Gerkens JF, Brash AR, Branch RA. Acute renal artery constriction increases renal prostaglandin I2 biosynthesis and renin release in the conscious dog. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1982;222:410–413. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

