Epidemiology of preterm birth
- PMID: 15374920
- PMCID: PMC517653
- DOI: 10.1136/bmj.329.7467.675
Epidemiology of preterm birth
Figures



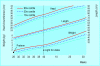
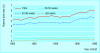
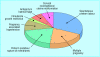


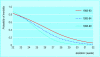
Comment in
-
Epidemiology of preterm birth: delayed cord clamping used to be taught and practised.BMJ. 2004 Nov 27;329(7477):1287; author reply 1287. doi: 10.1136/bmj.329.7477.1287. BMJ. 2004. PMID: 15564268 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Slattery M, Morrison JJ. Preterm delivery. Lancet 2002;360: 1489-97 - PubMed
-
- Kramer MS, Seguin L, Lydon, J, Goulet L. Socio-economic disparities in pregnancy outcome: why do the poor fare so poorly? Paediatr Perinat Epidemiol 2000;14: 194-210 - PubMed
-
- Wood NS, Marlow N, Costeloe K, Gibson AT, Wilkinson AR. Neurologic and developmental disability after extremely preterm birth. EPICure Study Group. N Engl J Med 2000;343: 378-84 - PubMed
-
- Lumley J, Oliver S, Waters E. Interventions for promoting smoking cessation during pregnancy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2000;2: CD001055. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
