Importance of Rhodospirillum rubrum H(+)-pyrophosphatase under low-energy conditions
- PMID: 15375148
- PMCID: PMC516592
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.186.19.6651-6655.2004
Importance of Rhodospirillum rubrum H(+)-pyrophosphatase under low-energy conditions
Abstract
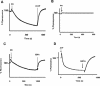
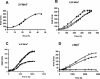
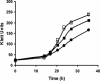
The physiological role of the membrane-bound pyrophosphatase of Rhodospirillum rubrum was investigated by the characterization of a mutant strain. Comparisons of growth levels between the wild type and the mutant under different low-potential conditions and during transitions between different metabolisms indicate that this enzyme provides R. rubrum with an alternative energy source that is important for growth in low-energy states.
Figures
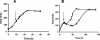
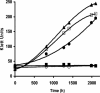
References
-
- Baltscheffsky, H., L. V. von Stedingk, H. W. Heldt, and M. Klingenberg. 1966. Inorganic pyrophosphate: formation in bacterial photophosphorylation. Science 153:1120-1122. - PubMed
-
- Baykov, A. A., N. V. Sergina, O. A. Evtushenko, and E. B. Dubnova. 1996. Kinetic characterization of the hydrolytic activity of the H+ pyrophosphatase of Rhodospirillum rubrum in membrane-bound and isolated states. Eur. J. Biochem. 236:121-127. - PubMed
-
- Celis, H., and I. Romero. 1987. The phosphate-pyrophosphate exchange and hydrolytic reactions of the membrane-bound pyrophosphatase of Rhodospirillum rubrum: effects of pH and divalent cations. J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 19:255-272. - PubMed
-
- Celis, H., B. Franco, S. Escobedo, and I. Romero. 2003. Rhodobacter sphaeroides has a family II pyrophosphatase. Comparison with other species of photosynthetic bacteria. Arch. Microbiol. 179:368-376. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

