Recent genetic transfer between Lactococcus lactis and enterobacteria
- PMID: 15375152
- PMCID: PMC516620
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.186.19.6671-6677.2004
Recent genetic transfer between Lactococcus lactis and enterobacteria
Abstract
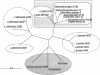
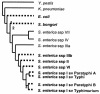
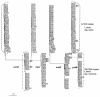
The genome sequence of Lactococcus lactis revealed that the ycdB gene was recently exchanged between lactococci and enterobacteria. The present study of ycdB orthologs suggests that L. lactis was probably the gene donor and reveals three instances of gene transfer to enterobacteria. Analysis of ycdB gene transfer between two L. lactis subspecies, L. lactis subsp. lactis and L. lactis subsp. cremoris, indicates that the gene can be mobilized, possibly by conjugation.
Figures


References
-
- Badger, J. H., and G. J. Olsen. 1999. CRITICA: coding region identification tool invoking comparative analysis. Mol. Biol. Evol. 16:512-524. - PubMed
-
- Berg, O. G., and C. G. Kurland. 2002. Evolution of microbial genomes: sequence acquisition and loss. Mol. Biol. Evol. 19:2265-2276. - PubMed
-
- Bolotin, A., S. D. Ehrlich, and A. Sorokin. 2002. Studies of genomes of dairy bacteria Lactococcus lactis. Sci. Aliment. 22:4-53.
MeSH terms
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

