Endonuclease-mediated mRNA decay requires tyrosine phosphorylation of polysomal ribonuclease 1 (PMR1) for the targeting and degradation of polyribosome-bound substrate mRNA
- PMID: 15375158
- PMCID: PMC1578673
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M409776200
Endonuclease-mediated mRNA decay requires tyrosine phosphorylation of polysomal ribonuclease 1 (PMR1) for the targeting and degradation of polyribosome-bound substrate mRNA
Abstract
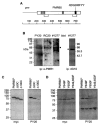
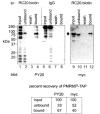
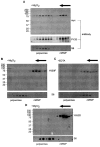
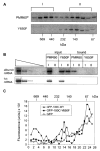
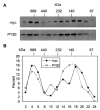
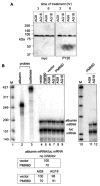
PMR1 is an endonuclease that is activated by estrogen to degrade Xenopus albumin mRNA. A previous report showed that the functional unit of endonuclease-mediated mRNA decay is a approximately 680-kDa polysome-bound complex that contains both PMR1 and substrate mRNA. PMR1 contains two domains involved in endonuclease targeting to polysomes, an N-terminal domain that lies between residues 200 and 250, and a C-terminal domain that lies within the last 100 residues. Loss of either domain inactivated PMR1 targeting to polysomes and stabilized albumin mRNA. The current study identified a phosphorylated tyrosine residue within the C-terminal polysome-targeting domain and showed that this modification is required for PMR1-mediated mRNA decay. Changing this tyrosine to phenylalanine inactivated the targeting of PMR1 to polysomes, blocked binding of PMR1 to the functional complex containing its substrate mRNA, prevented the targeting of a green fluorescent protein fusion protein to this complex, and stabilized albumin mRNA to degradation by PMR1 in vivo. A general tyrosine kinase inhibitor inhibited the phosphorylation of PMR1, which in turn inhibited PMR1-catalyzed degradation of albumin mRNA. These results indicate that one or more tyrosine kinases functions as a regulator of endonuclease-mediated mRNA decay.
Figures

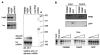
Similar articles
-
c-Src activates endonuclease-mediated mRNA decay.Mol Cell. 2007 Mar 9;25(5):779-87. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2007.01.026. Mol Cell. 2007. PMID: 17349962 Free PMC article.
-
Endonuclease-mediated mRNA decay involves the selective targeting of PMR1 to polyribosome-bound substrate mRNA.Mol Cell. 2004 May 21;14(4):435-45. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2004.05.001. Mol Cell. 2004. PMID: 15149593
-
The 90-kDa heat shock protein stabilizes the polysomal ribonuclease 1 mRNA endonuclease to degradation by the 26S proteasome.Mol Biol Cell. 2008 Feb;19(2):546-52. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e07-08-0774. Epub 2007 Nov 28. Mol Biol Cell. 2008. PMID: 18045990 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of endonuclease-mediated mRNA decay.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2011 Jul-Aug;2(4):582-600. doi: 10.1002/wrna.78. Epub 2011 Feb 10. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2011. PMID: 21957046 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Isolation of plant polysomal mRNA by differential centrifugation and ribosome immunopurification methods.Methods Mol Biol. 2009;553:109-26. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60327-563-7_6. Methods Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19588103 Review.
Cited by
-
Temporal dynamics of the Saccharopolyspora erythraea phosphoproteome.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2014 May;13(5):1219-30. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M113.033951. Epub 2014 Mar 10. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2014. PMID: 24615062 Free PMC article.
-
SMG6 cleavage generates metastable decay intermediates from nonsense-containing β-globin mRNA.PLoS One. 2013 Sep 25;8(9):e74791. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0074791. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24086375 Free PMC article.
-
Polysome-bound endonuclease PMR1 is targeted to stress granules via stress-specific binding to TIA-1.Mol Cell Biol. 2006 Dec;26(23):8803-13. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00090-06. Epub 2006 Sep 18. Mol Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16982678 Free PMC article.
-
c-Src activates endonuclease-mediated mRNA decay.Mol Cell. 2007 Mar 9;25(5):779-87. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2007.01.026. Mol Cell. 2007. PMID: 17349962 Free PMC article.
-
The cytoskeleton-associated Ena/VASP proteins are unanticipated partners of the PMR1 mRNA endonuclease.RNA. 2009 Apr;15(4):576-87. doi: 10.1261/rna.1206209. Epub 2009 Feb 17. RNA. 2009. PMID: 19223443 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

