Inhibitory modulation of distal C-terminal on protein kinase C-dependent phospho-regulation of rat TRPV1 receptors
- PMID: 15375192
- PMCID: PMC1665281
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2004.069054
Inhibitory modulation of distal C-terminal on protein kinase C-dependent phospho-regulation of rat TRPV1 receptors
Abstract
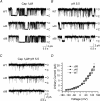
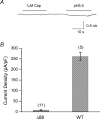
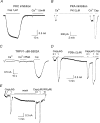
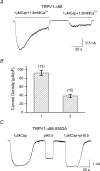
The vanilloid receptor TRPV1, previously known as VR1, has been implicated in pain sensation under both physiological and pathological conditions. The channel is highly expressed in sensory ganglion neurones and is activated by a range of noxious stimuli including irritant chemicals, acids and heat. In order to understand the structural basis underlying this polymodal activation and the regulation by intracellular signalling pathways, we have investigated the functional roles of the cytoplasmic C-terminal of rat TRPV1. A mutant with the maximal truncation of the distal C-terminal encompassing the last 88 residues was constructed. Of interest, this mutant exhibited a Ca(2+)-dependent functional loss; it was irresponsive to capsaicin in the presence of extracellular Ca(2+), but fully functional otherwise. Further studies of this construct revealed that extracellular Ca(2+) alone could activate the channel, and that the activation required protein kinase C (PKC) phosphorylation at S502, an event that was up-regulated by external Ca(2+) entry. We compared the truncation mutant with wild-type TRPV1 and demonstrated that it had a significantly increased sensitivity to PKC phosphorylation. These results suggest the distal C-terminal of TRPV1 can inhibit phosphorylation-induced potentiation of the wild-type channel. They also call into question some established functions of the distal C-terminal of TRPV1, including its roles in agonist binding and functional desensitization. We suggest that the functional loss of the truncation mutant, in the presence of extracellular Ca(2+), was not due to disruption of agonist binding or gating, but rather to desensitization promoted by unstimulated extracellular Ca(2+) entry.
Figures




References
-
- Bhave G, Zhu W, Wang H, Brasier DJ, Oxford GS, Gereau RW. cAMP-dependent protein kinase regulates desensitization of the capsaicin receptor (VR1) by direct phosphorylation. Neuron. 2002;35:721–731. - PubMed
-
- Caterina MJ, Leffler A, Malmberg AB, Martin WJ, Trafton J, Petersen-Zeitz KR, Koltzenburg M, Basbaum AI, Julius D. Impaired nociception and pain sensation in mice lacking the capsaicin receptor. Science. 2000;288:306–313. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

