Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) molecular signature in conjunctival mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) lymphoma
- PMID: 15375765
- PMCID: PMC1971129
- DOI: 10.14670/HH-19.1219
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) molecular signature in conjunctival mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) lymphoma
Abstract
Conjunctival mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) lymphoma is an extranodal marginal zone B-cell lymphoma that is characterized by an exaggerated clonal expansion of B cells, which implicate a pathological proliferative response to antigen(s) including bacteria. Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection is recognized as one of the causative agents of gastric MALT lymphoma; however, it has not been reported in extra gastric MALT lymphoma. We studied 5 patients (4 adults and 1 child) with salmon-colored conjunctival lesions. One patient also had a history of abnormal bone marrow biopsy a year earlier with lymphoid aggregates involving 5% of the overall bone marrow. The conjunctival lesions of the 5 patients were biopsied. Histopathological diagnoses were consistent with conjunctival MALT lymphoma. Lymphoma and normal conjunctival cells were microdissected using laser capture microscopy or manual techniques. DNA was extracted and subjected to PCR amplification using H. pylori gene-specific primers from the urease B and vac/m2 gene. Cells from chronic conjunctivitis (normal lymphocytes), conjunctival human T-cell lymphotropic virus type-1/adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma (HTLV-1/ATL), and orbital B-cell lymphoma were also microdissected, processed and analyzed. PCR amplification and Southern blot hybridization demonstrated H. pylori DNA in the conjunctival MALT lymphoma cells of 4/5 cases. The negative case was the one with a history of abnormal bone marrow. In contrast, H. pylori gene was not detected in normal conjunctival cells from the cases of MALT lymphoma or the lymphocytes, ATL and orbital B-lymphoma cells from the controls. These data suggest that H. pylori may play a role in conjunctival MALT lymphoma.
Figures



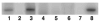
References
-
- Bayerdorffer E, Neubauer A, Rudolph B, Thiede C, Lehn N, Eidt S, Stolte M. Regression of primary gastric lymphoma of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue type after cure of Helicobacter pylori infection. MALT Lymphoma Study Group Lancet. 1995;345:1591–1594. - PubMed
-
- Bayerdorffer E, Miehlke S, Neubauer A, Stolte M. Gastric MALT-lymphoma and Helicobacter pylori infection. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 1997;1(11 Suppl):89–94. - PubMed
-
- Cavalli F, Isaacson PG, Gascoyne RD, Zucca E. MALT Lymphomas. Hematology (Am Soc Hematol Educ Program) . 2001:241–258. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
