Imaging native beta-actin mRNA in motile fibroblasts
- PMID: 15377515
- PMCID: PMC1304924
- DOI: 10.1529/biophysj.104.045153
Imaging native beta-actin mRNA in motile fibroblasts
Abstract
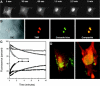
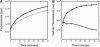
Nuclease-resistant, cytoplasmically resident molecular beacons were used to specifically label beta-actin mRNA in living and motile chicken embryonic fibroblasts. beta-actin mRNA signals were most abundant in active lamellipodia, which are protrusions that cells extend to adhere to surfaces. Time-lapse images show that the immediate sources of beta-actin mRNA for nascent lamellipodia are adjacent older protrusions. During the development of this method, we observed that conventional molecular beacons are rapidly sequestered in cell nuclei, leaving little time for them to find and bind to their cytoplasmic mRNA targets. By linking molecular beacons to a protein that tends to stay within the cytoplasm, nuclear sequestration was prevented, enabling cytoplasmic mRNAs to be detected and imaged. Probing beta-actin mRNA with these cytoplasmically resident molecular beacons did not affect the motility of the fibroblasts. Furthermore, mRNAs bound to these probes undergo translation within the cell. The use of cytoplasmically resident molecular beacons will enable further studies of the mechanism of beta-actin mRNA localization, and will be useful for understanding the dynamics of mRNA distribution in other living cells.
Figures
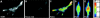
Similar articles
-
Single-molecule imaging of beta-actin mRNAs in the cytoplasm of a living cell.Exp Cell Res. 2009 Apr 15;315(7):1142-7. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2009.02.009. Epub 2009 Feb 23. Exp Cell Res. 2009. PMID: 19245805
-
Detection and localization of actin mRNA isoforms in chicken muscle cells by in situ hybridization using biotinated oligonucleotide probes.J Cell Biochem. 1990 Dec;44(4):241-52. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240440406. J Cell Biochem. 1990. PMID: 2095368
-
beta-Actin messenger RNA localization and protein synthesis augment cell motility.J Cell Biol. 1997 Mar 24;136(6):1263-70. doi: 10.1083/jcb.136.6.1263. J Cell Biol. 1997. PMID: 9087442 Free PMC article.
-
How and why does beta-actin mRNA target?Biol Cell. 2005 Jan;97(1):97-110. doi: 10.1042/BC20040063. Biol Cell. 2005. PMID: 15601261 Review.
-
[Cell polarity and actin mRNA localization].Med Sci (Paris). 2004 May;20(5):539-43. doi: 10.1051/medsci/2004205539. Med Sci (Paris). 2004. PMID: 15190471 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Single-cell detection of mRNA expression using nanofountain-probe electroporated molecular beacons.Small. 2015 May;11(20):2386-91. doi: 10.1002/smll.201401137. Epub 2015 Feb 1. Small. 2015. PMID: 25641752 Free PMC article.
-
Direct observation of cytoskeleton-dependent trafficking of miRNA visualized by the introduction of pre-miRNA.iScience. 2024 Jan 5;27(2):108811. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.108811. eCollection 2024 Feb 16. iScience. 2024. PMID: 38303695 Free PMC article.
-
Optical pretargeting of tumor with fluorescent MORF oligomers.Mol Imaging Biol. 2007 Jan-Feb;9(1):17-23. doi: 10.1007/s11307-006-0071-2. Mol Imaging Biol. 2007. PMID: 17171474
-
A molecular beacon-based approach for live-cell imaging of RNA transcripts with minimal target engineering at the single-molecule level.Sci Rep. 2017 May 8;7(1):1550. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-01740-1. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28484218 Free PMC article.
-
Use of flow cytometry for rapid, quantitative detection of poliovirus-infected cells via TAT peptide-delivered molecular beacons.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2013 Jan;79(2):696-700. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02429-12. Epub 2012 Nov 16. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23160127 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bertrand, E., P. Chartrand, M. Schaefer, S. M. Shenoy, R. H. Singer, and R. M. Long. 1998. Localization of ASH1 mRNA particles in living yeast. Mol. Cell. 2:437–445. - PubMed
-
- Dabauvalle, M. C., B. Schulz, U. Scheer, and R. Peters. 1988. Inhibition of nuclear accumulation of karyophilic proteins in living cells by microinjection of the lectin wheat germ agglutinin. Exp. Cell Res. 174:291–296. - PubMed
-
- Dias, N., and C. A. Stein. 2002. Antisense oligonucleotides: basic concepts and mechanisms. Mol. Cancer Ther. 1:347–355. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

