Hyper-inducible expression system for streptomycetes
- PMID: 15377796
- PMCID: PMC521115
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0406058101
Hyper-inducible expression system for streptomycetes
Abstract
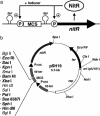
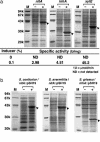
Streptomycetes produce useful enzymes and a wide variety of secondary metabolites with potent biological activities (e.g., antibiotics, immunosuppressors, pesticides, etc.). Despite their importance in the pharmaceutical and agrochemical fields, there have been no reports for practical expression systems in streptomycetes. Here, we developed a "P(nitA)-NitR" system for regulatory gene expression in streptomycetes based on the expression mechanism of Rhodococcus rhodochrous J1 nitrilase, which is highly induced by an inexpensive and safe inducer, epsilon-caprolactam. Heterologous protein expression experiments demonstrated that the system allowed suppressed basal expression and hyper-inducible expression, yielding target protein levels of as high as approximately 40% of all soluble protein. Furthermore, the system functioned in important streptomycete strains. Thus, the P(nitA)-NitR system should be a powerful tool for improving the productivity of various useful products in streptomycetes.
Figures

References
-
- Hopwood, D. A. (1999) Microbiology 145, 2183–2202. - PubMed
-
- Demain, A. L. & Fang, A. (2000) Adv. Biochem. Eng. Biotechnol. 69, 1–39. - PubMed
-
- Kieser, T., Bibb, M. J., Buttner, M. J., Chater, K. F. & Hopwood, D. A. (2000) Practical Streptomyces Genetics: A Laboratory Manual (The John Innes Foundation, Norwich, U.K.).
-
- Schmitt-John, T. & Engels, J. W. (1992) Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 36, 493–498. - PubMed
-
- Anne, J. & Van Mellaert, L. (1993) FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 114, 121–128. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

