Biology of recently discovered cytokines: discerning the pro- and anti-inflammatory properties of interleukin-27
- PMID: 15380038
- PMCID: PMC546292
- DOI: 10.1186/ar1227
Biology of recently discovered cytokines: discerning the pro- and anti-inflammatory properties of interleukin-27
Abstract
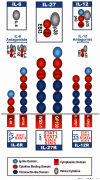
IL-27 is a recently identified heterodimeric cytokine produced in response to microbial and host derived inflammatory cues. Initial studies indicated that IL-27 promotes the generation of Th1 responses required for resistance to intracellular infection and unveiled the molecular mechanisms mediating this effect. However, subsequent work uncovered a role for IL-27 in the suppression of Th1 and Th2 responses. Thus, by discussing its pleotropic functions in the context of infection-induced immunity and by drawing parallels to fellow IL-6/IL-12 family cytokines, this review will attempt to reconcile the pro- and anti-inflammatory effects of IL-27.
Figures
References
-
- Villarino AV, Huang E, Hunter CA. Understanding the pro- and anti-inflammatory properties of IL-27. J Immunol. 2004;173:715–720. - PubMed
-
- Pflanz S, Timans JC, Cheung J, Rosales R, Kanzler H, Gilbert J, Hibbert L, Churakova T, Travis M, Vaisberg E, et al. IL-27, a heterodimeric cytokine composed of EBI3 and p28 protein, induces proliferation of naive CD4+ T cells. Immunity. 2002;16:779–790. doi: 10.1016/S1074-7613(02)00324-2. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

