How cellular movement determines the collective force generated by the Dictyostelium discoideum slug
- PMID: 15380385
- PMCID: PMC6457452
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2004.06.015
How cellular movement determines the collective force generated by the Dictyostelium discoideum slug
Abstract
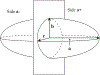
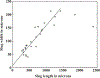
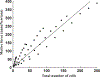
How the collective motion of cells in a biological tissue originates in the behavior of a collection of individuals, each of which responds to the chemical and mechanical signals it receives from neighbors, is still poorly understood. Here we study this question for a particular system, the slug stage of the cellular slime mold Dictyostelium discoideum (Dd). We investigate how cells in the interior of a migrating slug can effectively transmit stress to the substrate and thereby contribute to the overall motive force. Theoretical analysis suggests necessary conditions on the behavior of individual cells, and computational results shed light on experimental results concerning the total force exerted by a migrating slug. The model predicts that only cells in contact with the substrate contribute to the translational motion of the slug. Since the model is not based specifically on the mechanical properties of Dd cells, the results suggest that this behavior will be found in many developing systems.
Figures
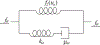

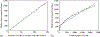
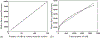
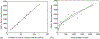
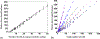


References
-
- Alberts B, Johnson A, Lewis J, Raff M, Roberts K, Walter P, 2002. Molecular Biology of the Cell, fourth ed. Garland, New York, London.
-
- Alt W, Dembo M, 1999. Cytoplasm dynamics and cell motion: two-phase flow models. Math. Biosci 156 (1), 207–228. - PubMed
-
- Beniot M, Gabriel D, Gerisch G, Gaub H, 2000. Discrete interactions in cell adhesion measured by single-molecule force spectroscopy. Nat. Cell Biol 2, 313–317. - PubMed
-
- Bonner JT, 1995. Why does slug length correlate with speed during migration in Dictyostelium discoideum?. J. Biosci 20 (1), 1–6.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

