Allergic sensitization enhances the contribution of Rho-kinase to airway smooth muscle contraction
- PMID: 15381630
- PMCID: PMC1575413
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705903
Allergic sensitization enhances the contribution of Rho-kinase to airway smooth muscle contraction
Abstract
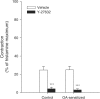
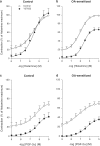
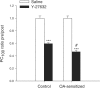
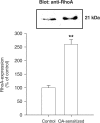
1. Repeated allergen challenge has been shown to increase the role of Rho-kinase in airway smooth muscle (ASM) contraction. We considered the possibility that active allergic sensitization by itself, that is, without subsequent allergen exposure, could be sufficient to enhance Rho-kinase-mediated ASM contraction. 2. Guinea pigs were actively IgE-sensitized to ovalbumin (OA), using Al(OH)(3) as adjuvant. Contractile responsiveness to G(q)-coupled receptor agonists (methacholine, histamine or PGF(2alpha)) was investigated in tracheal rings. No effect of sensitization was observed on basal- and methacholine-induced myogenic tone. In contrast, potency of histamine and PGF(2alpha) increased, that is, EC(50) decreased, after OA-sensitization by 2.6- and 4.7-fold, respectively, without effect on maximal contraction (E(max)). 3. Basal tone in preparations from both control and OA-sensitized animals was strongly decreased in the presence of the Rho-kinase inhibitor (+)-(R)-trans-4-(1-aminoethyl)-N-(4-pyridyl) cyclohexane carboxamide (Y-27632) (1 microm). In control preparations, the E(max) and potency of histamine were unaffected by Y-27632, but were decreased for PGF(2alpha) (by 38.2% and 2.0-fold, respectively). However, in preparations from OA-sensitized animals, Y-27632 induced a significant reduction in E(max) (33.5%) and potency (2.3-fold) of histamine and of PGF(2alpha) (48.3% and 6.6-fold, respectively), normalizing the OA-sensitization-induced increase in sensitivity toward these agonists. 4. We also investigated the contribution of Rho-kinase in vivo by measuring airway responsiveness toward inhaled histamine in permanently instrumented, unanaesthetized control and OA-sensitized guinea pigs. Treatment with Y-27632 by inhalation (5 mm, nebulizer concentration) decreased airway responsiveness toward histamine both in control and OA-sensitized animals. However, the histamine PC(100) ratio pre/post Y-27632 inhalation was significantly smaller in OA-sensitized animals as compared to control animals, indicating an enhanced contribution of Rho-kinase. 5. Expression of RhoA, an upstream activator of Rho-kinase, was significantly increased (2.6-fold) in lung homogenates of OA-sensitized guinea pigs compared to control animals, as determined by Western analysis. 6. In conclusion, the results show a receptor-dependent role of Rho-kinase in agonist-induced ASM contraction. The contribution of Rho-kinase to contractile airway responsiveness, both in vivo and ex vivo, is augmented after active allergic sensitization, as a consequence of increased expression of RhoA presumably. Inhibition of the RhoA/Rho-kinase pathway may be considered a useful pharmacotherapeutical target in allergy and asthma.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Inhalation of the Rho-kinase inhibitor Y-27632 reverses allergen-induced airway hyperresponsiveness after the early and late asthmatic reaction.Respir Res. 2006 Sep 26;7(1):121. doi: 10.1186/1465-9921-7-121. Respir Res. 2006. PMID: 17002806 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of Rho-kinase normalizes nonspecific hyperresponsiveness in passively sensitized airway smooth muscle preparations.Eur J Pharmacol. 2006 Feb 15;531(1-3):145-50. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2005.12.043. Epub 2006 Jan 31. Eur J Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16451800
-
Role of contractile prostaglandins and Rho-kinase in growth factor-induced airway smooth muscle contraction.Respir Res. 2005 Jul 27;6(1):85. doi: 10.1186/1465-9921-6-85. Respir Res. 2005. PMID: 16048647 Free PMC article.
-
[Novel mechanisms for increasing Ca2+ sensitivity of contractile apparatus in smooth muscle].Masui. 1998 May;47(5):530-40. Masui. 1998. PMID: 9621661 Review. Japanese.
-
The role of RhoA-mediated Ca2+ sensitization of bronchial smooth muscle contraction in airway hyperresponsiveness.J Smooth Muscle Res. 2004 Oct;40(4-5):155-67. doi: 10.1540/jsmr.40.155. J Smooth Muscle Res. 2004. PMID: 15655303 Review.
Cited by
-
Ras homolog family member A/Rho-associated protein kinase 1 signaling modulates lineage commitment of mesenchymal stem cells in asthmatic patients through lymphoid enhancer-binding factor 1.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2019 Apr;143(4):1560-1574.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2018.08.023. Epub 2018 Sep 5. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30194990 Free PMC article.
-
Airway smooth muscle in the pathophysiology and treatment of asthma.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2013 Apr;114(7):834-43. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00950.2012. Epub 2013 Jan 10. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2013. PMID: 23305987 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A novel biased allosteric compound inhibitor of parturition selectively impedes the prostaglandin F2alpha-mediated Rho/ROCK signaling pathway.J Biol Chem. 2010 Aug 13;285(33):25624-36. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.115196. Epub 2010 Jun 15. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20551320 Free PMC article.
-
Inhalation of the Rho-kinase inhibitor Y-27632 reverses allergen-induced airway hyperresponsiveness after the early and late asthmatic reaction.Respir Res. 2006 Sep 26;7(1):121. doi: 10.1186/1465-9921-7-121. Respir Res. 2006. PMID: 17002806 Free PMC article.
-
Muscarinic receptor signaling in the pathophysiology of asthma and COPD.Respir Res. 2006 May 9;7(1):73. doi: 10.1186/1465-9921-7-73. Respir Res. 2006. PMID: 16684353 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- AMMIT A.J., ARMOUR C.L., BLACK J.L. Smooth-muscle myosin light-chain kinase content is increased in human sensitized airways. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2000;161:257–263. - PubMed
-
- BLACK J.L., MARTHAN R., ARMOUR C.L., JOHNSON P.R. Sensitization alters contractile responses and calcium influx in human airway smooth muscle. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1989;84:440–447. - PubMed
-
- BRADFORD M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976;72:248–254. - PubMed
-
- BRAMLEY A.M., THOMSON R.J., ROBERTS C.R., SCHELLENBERG R.R. Hypothesis: excessive bronchoconstriction in asthma is due to decreased airway elastance. Eur. Respir. J. 1994;7:337–341. - PubMed
-
- CERRINA J., LABAT C., HAYE-LEGRANDE I., RAFFESTIN B., BENVENISTE J., BRINK C. Human isolated bronchial muscle preparations from asthmatic patients: effects of indomethacin and contractile agonists. Prostaglandins. 1989;37:457–469. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

