Differential dynamics of histone H3 methylation at positions K4 and K9 in the mouse zygote
- PMID: 15383155
- PMCID: PMC521682
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-213X-4-12
Differential dynamics of histone H3 methylation at positions K4 and K9 in the mouse zygote
Abstract
Background: In the mouse zygote the paternal genome undergoes dramatic structural and epigenetic changes. Chromosomes are decondensed, protamines replaced by histones and DNA is rapidly and actively demethylated. The epigenetic asymmetry between parental genomes remains at least until the 2-cell stage suggesting functional differences between paternal and maternal genomes during early cleavage stages.
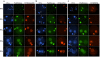
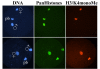
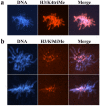
Results: Here we analyzed the timing of histone deposition on the paternal pronucleus and the dynamics of histone H3 methylation (H3/K4mono-, H3/K4tri- and H3/K9di-methylation) immediately after fertilization. Whereas maternal chromatin maintains all types of histone H3 methylation throughout the zygotic development, paternal chromosomes acquire new and unmodified histones shortly after fertilization. In the following hours we observe a gradual increase in H3/K4mono-methylation whereas H3/K4tri-methylation is not present before latest pronuclear stages. Histone H3/K9di-methylation is completely absent from the paternal pronucleus, including metaphase chromosomes of the first mitotic stage.
Conclusion: Parallel to the epigenetic asymmetry in DNA methylation, chromatin modifications are also different between both parental genomes in the very first hours post fertilization. Whereas methylation at H3/K4 gradually becomes similar between both genomes, H3/K9 methylation remains asymmetric.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

