Differential expression of Toll-like receptors 2 and 4 in tissues of the human female reproductive tract
- PMID: 15385480
- PMCID: PMC517561
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.72.10.5799-5806.2004
Differential expression of Toll-like receptors 2 and 4 in tissues of the human female reproductive tract
Abstract
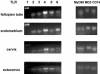
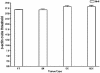
Toll-like receptor (TLR) signal transduction is a central component of the innate immune response to pathogenic challenge. Although recent studies have begun to elucidate differences in acquired immunity in tissues of the human female reproductive tract, there is a relative paucity of work regarding innate defense mechanisms. We investigated TLR mRNA and protein expression in tissues of the human female reproductive tract. Constitutive mRNA expression of TLRs 1 to 6 was observed in fallopian tubes, uterine endometrium, cervix, and ectocervix. Furthermore, transcripts of the signaling adapter MyD88 and the accessory molecule CD14 were also detected in all tissues assayed. Quantitative analysis of TLR2 mRNA levels revealed highest expression of this molecule in fallopian tube and cervical tissues, followed by endometrium and ectocervix. In contrast to TLR2, TLR4 expression declined progressively along the tract, with highest expression in the upper tissues (fallopian tubes and endometrium), followed by cervix and ectocervix. In addition to mRNA, protein expression of TLR2 and TLR4 was also documented in these tissues. These data suggest that TLRs are differentially expressed in distinct compartments of the female reproductive tract and may provide insight regarding the regulation of inflammation and immunity within the tract.
Figures
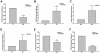
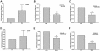
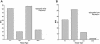
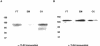
References
-
- Barlow, R. E., I. D. Cooke, O. Odukoya, M. Heatley, J. Jenkins, G. Narayansingh, S. S. Ramsewak, and A. Eley. 2001. The prevalence of Chlamydia trachomatis in fresh tissue specimens from patients with ectopic pregnancy or tubal factor infertility as determined by PCR and in-situ hybridisation. J. Med. Microbiol. 50:902-908. - PubMed
-
- Bowie, A., and L. A. O'Neill. 2000. The interleukin-1 receptor/Toll-like receptor superfamily: signal generators for pro-inflammatory interleukins and microbial products. J. Leukoc. Biol. 67:508-514. - PubMed
-
- Darville, T., J. M. O'Neill, C. W. Andrews, Jr., U. M. Nagarajan, L. Stahl, and D. M. Ojcius. 2003. Toll-like receptor-2, but not toll-like receptor-4, is essential for development of oviduct pathology in chlamydial genital tract infection. J. Immunol. 171:6187-6197. - PubMed
-
- Eggert-Kruse, W., Reimann-Andersen, J., G. Rohr, S. Pohl, W. Tilgen, and B. Runnebaum. 1995. Clinical relevance of sperm morphology assessment using strict criteria and relationship with sperm-mucus interaction in vivo and in vitro. Fertil. Steril. 63:612-624. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

