Theta-modulated place-by-direction cells in the hippocampal formation in the rat
- PMID: 15385610
- PMCID: PMC2683733
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2635-04.2004
Theta-modulated place-by-direction cells in the hippocampal formation in the rat
Abstract
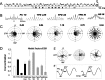
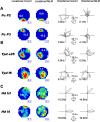
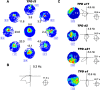
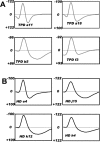
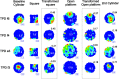
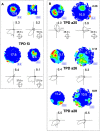
We report the spatial and temporal properties of a class of cells termed theta-modulated place-by-direction (TPD) cells recorded from the presubicular and parasubicular cortices of the rat. The firing characteristics of TPD cells in open-field enclosures were compared with those of the following two other well characterized cell classes in the hippocampal formation: place and head-direction cells. Unlike place cells, which code only for the animal's location, or head-direction cells, which code only for the animal's directional heading, TPD cells code for both the location and the head direction of the animal. Their firing is also strongly theta modulated, firing primarily at the negative-to-positive phase of the locally recorded theta wave. TPD theta modulation is significantly stronger than that of place cells. In contrast, the firing of head-direction cells is not modulated by theta at all. In repeated exposures to the same environment, the locational and directional signals of TPD cells are stable. When recorded in different environments, TPD locational and directional fields can uncouple, with the locational field shifting unpredictably ("remapping"), whereas the directional preference remains similar across environments.
Figures

References
-
- Barnes CA (1988) Spatial learning and memory processes: the search for their neurobiological mechanisms in the rat. Trends Neurosci 11: 163-169. - PubMed
-
- Bischof WF, Boulanger P (2003) Spatial navigation in virtual reality environments: an EEG analysis. Cyberpsychol Behav 6: 487-495. - PubMed
-
- Bland BH, Colom LV (1993) Extrinsic properties underlying oscillation and synchrony in the limbic cortex. Prog Neurobiol 2: 152-208. - PubMed
-
- Bland BH, Oddie SD (2001) Theta band oscillation and synchrony in the hippocampal formation and associated structures: the case for its role in sensorimotor integration. Behav Brain Res 127: 119-136. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
