Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activates ERK in primary sensory neurons and mediates inflammatory heat hyperalgesia through TRPV1 sensitization
- PMID: 15385613
- PMCID: PMC6729698
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2893-04.2004
Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activates ERK in primary sensory neurons and mediates inflammatory heat hyperalgesia through TRPV1 sensitization
Abstract
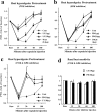
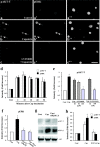
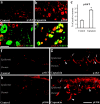
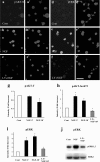
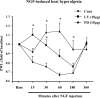
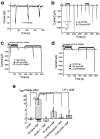
Although the PI3K (phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase) pathway typically regulates cell growth and survival, increasing evidence indicates the involvement of this pathway in neural plasticity. It is unknown whether the PI3K pathway can mediate pain hypersensitivity. Intradermal injection of capsaicin and NGF produce heat hyperalgesia by activating their respective TRPV1 (transient receptor potential vanilloid receptor-1) and TrkA receptors on nociceptor sensory nerve terminals. We examined the activation of PI3K in primary sensory DRG neurons by these inflammatory agents and the contribution of PI3K activation to inflammatory pain. We further investigated the correlation between the PI3K and the ERK (extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase) pathway. Capsaicin and NGF induce phosphorylation of the PI3K downstream target AKT (protein kinase B), which is blocked by the PI3K inhibitors LY294002 and wortmannin, indicative of the activation of PI3K by both agents. ERK activation by capsaicin and NGF was also blocked by PI3K inhibitors. Similarly, intradermal capsaicin in rats activated PI3K and ERK in C-fiber DRG neurons and epidermal nerve fibers. Injection of PI3K or MEK (ERK kinase) inhibitors into the hindpaw attenuated capsaicin- and NGF-evoked heat hyperalgesia but did not change basal heat sensitivity. Furthermore, PI3K, but not ERK, inhibition blocked early induction of hyperalgesia. In acutely dissociated DRG neurons, the capsaicin-induced TRPV1 current was strikingly potentiated by NGF, and this potentiation was completely blocked by PI3K inhibitors and primarily suppressed by MEK inhibitors. Therefore, PI3K induces heat hyperalgesia, possibly by regulating TRPV1 activity, in an ERK-dependent manner. The PI3K pathway also appears to play a role that is distinct from ERK by regulating the early onset of inflammatory pain.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Regulation of transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily V1 protein synthesis by the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt pathway in colonic hypersensitivity.Exp Neurol. 2017 Sep;295:104-115. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2017.06.007. Epub 2017 Jun 3. Exp Neurol. 2017. PMID: 28587873 Free PMC article.
-
Activity-dependent phosphorylation of Akt/PKB in adult DRG neurons.Eur J Neurosci. 2005 Apr;21(7):1785-97. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2005.04011.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2005. PMID: 15869474
-
Activation of CB1 inhibits NGF-induced sensitization of TRPV1 in adult mouse afferent neurons.Neuroscience. 2014 Sep 26;277:679-89. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2014.07.041. Epub 2014 Aug 1. Neuroscience. 2014. PMID: 25088915 Free PMC article.
-
Neurotrophic Factors and Nociceptor Sensitization.In: Kruger L, Light AR, editors. Translational Pain Research: From Mouse to Man. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2010. Chapter 2. In: Kruger L, Light AR, editors. Translational Pain Research: From Mouse to Man. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2010. Chapter 2. PMID: 21882462 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Nociception and TRP Channels.Curr Drug Targets CNS Neurol Disord. 2004 Dec;3(6):479-85. doi: 10.2174/1568007043336789. Curr Drug Targets CNS Neurol Disord. 2004. PMID: 15578965 Review.
Cited by
-
Formaldehyde up-regulates TRPV1 through MAPK and PI3K signaling pathways in a rat model of bone cancer pain.Neurosci Bull. 2012 Apr;28(2):165-72. doi: 10.1007/s12264-012-1211-0. Neurosci Bull. 2012. PMID: 22466127 Free PMC article.
-
Preso1, mGluR5 and the machinery of pain.Nat Neurosci. 2012 May 25;15(6):805-7. doi: 10.1038/nn.3118. Nat Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22627790 Free PMC article.
-
The mechanism of μ-opioid receptor (MOR)-TRPV1 crosstalk in TRPV1 activation involves morphine anti-nociception, tolerance and dependence.Channels (Austin). 2015;9(5):235-43. doi: 10.1080/19336950.2015.1069450. Epub 2015 Jul 15. Channels (Austin). 2015. PMID: 26176938 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intracellular emetic signaling cascades by which the selective neurokinin type 1 receptor (NK1R) agonist GR73632 evokes vomiting in the least shrew (Cryptotis parva).Neurochem Int. 2019 Jan;122:106-119. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2018.11.012. Epub 2018 Nov 16. Neurochem Int. 2019. PMID: 30453005 Free PMC article.
-
Translating nociceptive processing into human pain models.Exp Brain Res. 2009 Jun;196(1):173-8. doi: 10.1007/s00221-009-1809-2. Epub 2009 Apr 29. Exp Brain Res. 2009. PMID: 19404625 Review.
References
-
- Amadesi S, Nie J, Vergnolle N, Cottrell GS, Grady EF, Trevisani M, Manni C, Geppetti P, McRoberts JA, Ennes H, Davis JB, Mayer EA, Bunnett NW (2004) Protease-activated receptor 2 sensitizes the capsaicin receptor transient receptor potential vanilloid receptor 1 to induce hyperalgesia. J Neurosci 24: 4300-4312. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Atwal JK, Massie B, Miller FD, Kaplan DR (2000) The TrkB-Shc site signals neuronal survival and local axon growth via MEK and P13-kinase. Neuron 27: 265-277. - PubMed
-
- Bandell M, Story GM, Hwang SW, Viswanath V, Eid SR, Petrus MJ, Earley TJ, Patapoutian A (2004) Noxious cold ion channel TRPA1 is activated by pungent compounds and bradykinin. Neuron 41: 849-857. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
