Influence of serum cholesterol on atherogenesis and intimal hyperplasia after angioplasty: inhibition by amlodipine
- PMID: 15388506
- PMCID: PMC4732715
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00617.2004
Influence of serum cholesterol on atherogenesis and intimal hyperplasia after angioplasty: inhibition by amlodipine
Abstract
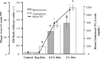
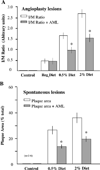
The objectives of the present study were to determine whether serum hypercholesterolemia (HC) promotes the development of spontaneous and angioplasty-induced lesions and whether amlodipine inhibits these lesions and cellular processes underlying their genesis. Rabbits were fed normal, 0.5%, or 2% cholesterol diets for 9 wk, which resulted in the development of increasing HC. After week one, balloon dilation of the abdominal aorta was performed while the thoracic aorta was not disturbed and monitored for the development of spontaneous lesions. Lesion size increased with the degree of HC and was accompanied by increased collagen synthesis and smooth muscle cell (SMC) proliferation at each site. Amlodipine (5 mg/kg p.o.) inhibited lesion size by 50% (P < 0.01) at both sites in cholesterol-fed animals but not at angioplasty sites in animals on a normal diet. Local collagen synthesis was inhibited at both sites by amlodipine in the diet animals. The increase in HC was accompanied by a 1.7-fold increase in basal Ca2+ uptake in SMCs in the thoracic aorta, which was not altered by amlodipine, nifedipine, Ni2+, or La3+, revealing an uninhibitable calcium leak during atherogenesis. In culture, cholesterol enrichment increased SMC proliferation, collagen synthesis, and the secretion of a soluble SMC mitogen, which were inhibited by amlodipine (10(-9) M). Finally, in SMC membranes, amlodipine uniquely restored the cholesterol-expanded membrane bilayer width without any effect on membrane fluidity. This study establishes a causal role between serum HC and the development of spontaneous and angioplasty-induced lesions and the ability of amlodipine to disrupt this action by a novel remodelling action on the SMC membrane.
Figures



References
-
- Bligh EG, Dyer WJ. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem. 1959;37:911–917. - PubMed
-
- Boesze-Battaglia K, Schimmel R. Cell membrane lipid composition and distribution: implications for cell function and lessons learned from photoreceptors and platelets. J Exp Biol. 1997;200:2927–2936. - PubMed
-
- Byington R, Riley W, Booth D, Herrington D, Hunninghake D, Mallon S, Miller M, Ramanathan K, Werns S, Furberg C, Pitt B. Effect of amlodipine on progression of carotid atherosclerosis in patients with documented heart disease. Am J Hypertens. 1999;12:42A–43A.
-
- Chen M, Mason RP, Tulenko TN. Atherosclerosis alters composition, structure and function of arterial smooth muscle plasma membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1995;1272:101–112. - PubMed
-
- Chou T, Yang S, Pei D. Amlodipine inhibits pro-inflammatory cytokines and free radical production and inducible nitric oxide synthase expression in lipopolysaccharide/interferon-gamma-stimulated cultured vascular smooth muscle cells. Jpn J Pharmacol. 2002;89:157–163. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

