From quantitative microscopy to automated image understanding
- PMID: 15447010
- PMCID: PMC1458526
- DOI: 10.1117/1.1779233
From quantitative microscopy to automated image understanding
Abstract
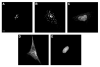
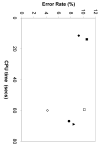
Quantitative microscopy has been extensively used in biomedical research and has provided significant insights into structure and dynamics at the cell and tissue level. The entire procedure of quantitative microscopy is comprised of specimen preparation, light absorption/reflection/emission from the specimen, microscope optical processing, optical/electrical conversion by a camera or detector, and computational processing of digitized images. Although many of the latest digital signal processing techniques have been successfully applied to compress, restore, and register digital microscope images, automated approaches for recognition and understanding of complex subcellular patterns in light microscope images have been far less widely used. We describe a systematic approach for interpreting protein subcellular distributions using various sets of subcellular location features (SLF), in combination with supervised classification and unsupervised clustering methods. These methods can handle complex patterns in digital microscope images, and the features can be applied for other purposes such as objectively choosing a representative image from a collection and performing statistical comparisons of image sets.
(c) 2004 Society of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers.
Figures










References
-
- Macbeath G. Protein microarrays and proteomics. Nature Genetics. 2002;32:526–532. - PubMed
-
- Cutler P. Protein arrays: The current state-of-the-art. Proteomics. 2003;3:3–18. - PubMed
-
- Sali A, Glaeser R, Earnest T, Baumeister W. From words to literature in structural proteomics. Nature. 2003;422:216–225. - PubMed
-
- Ghaemmaghami S, Huh WK, Bower K, Howson RW, Belle A, Dephoure N, O'Shea EK, Weissman JS. Global analysis of protein expression in yeast. Nature. 2003;425:737–41. - PubMed
-
- Chen X, Velliste M, Weinstein S, Jarvik JW, Murphy RF. Location proteomics - Building subcellular location trees from high resolution 3D fluorescence microscope images of randomly-tagged proteins. Proc. SPIE. 2003;4962:298–306.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

