Identification of tyrosine hydroxylase as a physiological substrate for Cdk5
- PMID: 15447670
- PMCID: PMC1855259
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2004.02723.x
Identification of tyrosine hydroxylase as a physiological substrate for Cdk5
Abstract
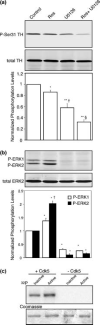
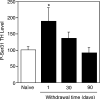
Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 (Cdk5) is emerging as a neuronal protein kinase involved in multiple aspects of neurotransmission in both post- and presynaptic compartments. Within the reward/motor circuitry of the basal ganglia, Cdk5 regulates dopamine neurotransmission via phosphorylation of the postsynaptic signal transduction pathway integrator, DARPP-32 (dopamine- and cyclic AMP-regulated phosphoprotein, M(r) 32,000). Cdk5 has also been implicated in regulating various steps in the presynaptic vesicle cycle. Here we report that Cdk5 phosphorylates tyrosine hydroxylase (TH), the key enzyme for synthesis of dopamine. Using phosphopeptide mapping, site-directed mutagenesis, and phosphorylation state-specific antibodies, the site was identified as Ser31, a previously defined extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1/2 (ERK1/2) site. The phosphorylation of Ser31 by Cdk5 versus ERK1/2 was investigated in intact mouse striatal tissue using a pharmacological approach. The results indicated that Cdk5 phosphorylates TH directly and also regulates ERK1/2-dependent phosphorylation of TH through the phosphorylation of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1 (MEK1). Finally, phospho-Ser31 TH levels were increased in dopaminergic neurons of rats trained to chronically self-administer cocaine. These results demonstrate direct and indirect regulation of the phosphorylation state of a Cdk5/ERK1/2 site on TH and suggest a role for these pathways in the neuroadaptive changes associated with chronic cocaine exposure.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1 and 2 by depolarization stimulates tyrosine hydroxylase phosphorylation and dopamine synthesis in rat brain.Eur J Neurosci. 2002 Feb;15(4):769-73. doi: 10.1046/j.1460-9568.2002.01901.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2002. PMID: 11886455
-
Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 regulates dopaminergic and glutamatergic transmission in the striatum.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Feb 17;101(7):2191-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0308652100. Epub 2004 Feb 9. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004. PMID: 14769920 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation of DARPP-32 by Cdk5 modulates dopamine signalling in neurons.Nature. 1999 Dec 9;402(6762):669-71. doi: 10.1038/45251. Nature. 1999. PMID: 10604473
-
Neuronal cyclin-dependent kinase 5: role in nervous system function and its specific inhibition by the Cdk5 inhibitory peptide.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004 Mar 11;1697(1-2):143-53. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2003.11.020. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004. PMID: 15023357 Review.
-
The role of DARPP-32 in the actions of drugs of abuse.Neuropharmacology. 2004;47 Suppl 1:14-23. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2004.05.010. Neuropharmacology. 2004. PMID: 15464122 Review.
Cited by
-
Tyrosine hydroxylase phosphorylation in catecholaminergic brain regions: a marker of activation following acute hypotension and glucoprivation.PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e50535. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0050535. Epub 2012 Nov 29. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23209770 Free PMC article.
-
Progesterone decreases tyrosine hydroxylase phosphorylation state and increases protein phosphatase 2A activity in the stalk-median eminence on proestrous afternoon.J Endocrinol. 2010 Feb;204(2):209-19. doi: 10.1677/JOE-09-0335. Epub 2009 Nov 27. J Endocrinol. 2010. PMID: 19945993 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative trait locus analysis identifies rat genomic regions related to amphetamine-induced locomotion and Galpha(i3) levels in nucleus accumbens.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2008 Oct;33(11):2735-46. doi: 10.1038/sj.npp.1301667. Epub 2008 Jan 23. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2008. PMID: 18216777 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 in the ventral tegmental area regulates depression-related behaviors.J Neurosci. 2014 Apr 30;34(18):6352-66. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3673-13.2014. J Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24790206 Free PMC article.
-
Cdk5 Modulates Long-Term Synaptic Plasticity and Motor Learning in Dorsolateral Striatum.Sci Rep. 2016 Jul 22;6:29812. doi: 10.1038/srep29812. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27443506 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Almas B, Le Bourdelles B, Flatmark T, Mallet J, Haavik J. Regulation of recombinant human tyrosine hydroxylase isozymes by catecholamine binding and phosphorylation. Structure/activity studies and mechanistic implications. Eur. J. Biochem. 1992;209:249–255. - PubMed
-
- Beitner-Johnson D, Nestler EJ. Morphine and cocaine exert common chronic actions on tyrosine hydroxylase in dopaminergic brain reward regions. J. Neurochem. 1991;57:344–347. - PubMed
-
- Bevilaqua LRM, Graham ME, Dunkley PR, von Nagy-Felsobuki EI, Dickson PW. Phosphorylation of Ser19 alters the conformation of tyrosine hydroxylase to increase the rate of phosphorylation of ser40. J. Biol. Chem. 2001;276:40 411–40 416. - PubMed
-
- Bibb JA. Role of cdk5 in neuronal signaling, plasticity, and drug abuse. Neurosignals. 2003;12:191–199. - PubMed
-
- Bibb JA, da Cruz e Silva EF. Identification of posttranslational modification sites by site-directed mutagenesis. In: Hemmings HCJ, editor. Neuromethods. Vol. 30. Humana Press Inc.; Totowa, N.J.: 1996. pp. 275–307. Regulatory Protein Modification: Techniques and Protocols.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

