Heavy metal stress. Activation of distinct mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways by copper and cadmium
- PMID: 15448198
- PMCID: PMC523386
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.104.045724
Heavy metal stress. Activation of distinct mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways by copper and cadmium
Abstract
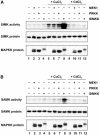
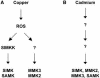
Excessive amounts of heavy metals adversely affect plant growth and development. Whereas some regions naturally contain high levels of heavy metals, anthropogenic release of heavy metals into the environment continuously increases soil contamination. The presence of elevated levels of heavy metal ions triggers a wide range of cellular responses including changes in gene expression and synthesis of metal-detoxifying peptides. To elucidate signal transduction events leading to the cellular response to heavy metal stress we analyzed protein phosphorylation induced by elevated levels of copper and cadmium ions as examples for heavy metals with different physiochemical properties and functions. Exposure of alfalfa (Medicago sativa) seedlings to excess copper or cadmium ions activated four distinct mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs): SIMK, MMK2, MMK3, and SAMK. Comparison of the kinetics of MAPK activation revealed that SIMK, MMK2, MMK3, and SAMK are very rapidly activated by copper ions, while cadmium ions induced delayed MAPK activation. In protoplasts, the MAPK kinase SIMKK specifically mediated activation of SIMK and SAMK but not of MMK2 and MMK3. Moreover, SIMKK only conveyed MAPK activation by CuCl(2) but not by CdCl(2). These results suggest that plants respond to heavy metal stress by induction of several distinct MAPK pathways and that excess amounts of copper and cadmium ions induce different cellular signaling mechanisms in roots.
Figures

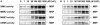



Similar articles
-
Convergence and divergence of stress-induced mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathways at the level of two distinct mitogen-activated protein kinase kinases.Plant Cell. 2002 Mar;14(3):703-11. Plant Cell. 2002. PMID: 11910015 Free PMC article.
-
SIMKK, a mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) kinase, is a specific activator of the salt stress-induced MAPK, SIMK.Plant Cell. 2000 Nov;12(11):2247-58. doi: 10.1105/tpc.12.11.2247. Plant Cell. 2000. PMID: 11090222 Free PMC article.
-
Differential activation of four specific MAPK pathways by distinct elicitors.J Biol Chem. 2000 Nov 24;275(47):36734-40. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M007418200. J Biol Chem. 2000. PMID: 10973984
-
Plant responses to abiotic stresses: heavy metal-induced oxidative stress and protection by mycorrhization.J Exp Bot. 2002 May;53(372):1351-65. J Exp Bot. 2002. PMID: 11997381 Review.
-
The role of metals in modulating metalloprotease activity in the AD brain.Eur Biophys J. 2008 Mar;37(3):315-21. doi: 10.1007/s00249-007-0244-1. Epub 2008 Feb 13. Eur Biophys J. 2008. PMID: 18270696 Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanisms on boron-induced alleviation of aluminum-toxicity in Citrus grandis seedlings at a transcriptional level revealed by cDNA-AFLP analysis.PLoS One. 2015 Mar 6;10(3):e0115485. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0115485. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25747450 Free PMC article.
-
Cadmium hijacks the high zinc response by binding and activating the HIZR-1 nuclear receptor.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Oct 19;118(42):e2022649118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2022649118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 34649987 Free PMC article.
-
Zinc and Copper Enhance Cucumber Tolerance to Fusaric Acid by Mediating Its Distribution and Toxicity and Modifying the Antioxidant System.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 May 10;21(9):3370. doi: 10.3390/ijms21093370. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32397623 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of transcriptional and upstream regulatory sequence activity of two environmental stress-inducible genes, NBS-Str1 and BLEC-Str8, of rice.Transgenic Res. 2012 Apr;21(2):351-66. doi: 10.1007/s11248-011-9535-5. Epub 2011 Jul 3. Transgenic Res. 2012. PMID: 21725856
-
MAPKs regulate root growth by influencing auxin signaling and cell cycle-related gene expression in cadmium-stressed rice.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2013 Aug;20(8):5449-60. doi: 10.1007/s11356-013-1559-3. Epub 2013 Feb 21. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2013. PMID: 23430734
References
-
- Agrawal GK, Iwahashi H, Rakwal R (2003) Rice MAPKs. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 302: 171–180 - PubMed
-
- Avery SV (2001) Metal toxicity in yeasts and the role of oxidative stress. Adv Appl Microbiol 49: 111–142 - PubMed
-
- Bögre L, Ligterink W, Heberle-Bors E, Hirt H (1996) Mechanosensors in plants. Nature 383: 489–490 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

