A poxvirus protein forms a complex with left-handed Z-DNA: crystal structure of a Yatapoxvirus Zalpha bound to DNA
- PMID: 15448208
- PMCID: PMC521960
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0405586101
A poxvirus protein forms a complex with left-handed Z-DNA: crystal structure of a Yatapoxvirus Zalpha bound to DNA
Abstract
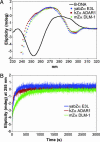
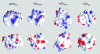
A conserved feature of poxviruses is a protein, well characterized as E3L in vaccinia virus, that confers IFN resistance on the virus. This protein comprises two domains, an N-terminal Z-DNA-binding protein domain (Zalpha) and a C-terminal double-stranded RNA-binding domain. Both are required for pathogenicity of vaccinia virus in mice infected by intracranial injection. Here, we describe the crystal structure of the Zalpha domain from the E3L-like protein of Yaba-like disease virus, a Yatapoxvirus, in a complex with Z-DNA, solved at a 2.0-A resolution. The DNA contacting surface of Yaba-like disease virus Zalpha(E3L) closely resembles that of other structurally defined members of the Zalpha family, although some variability exists in the beta-hairpin region. In contrast to the Z-DNA-contacting surface, the nonbinding surface of members of the Zalpha family are unrelated; this surface may effect protein-specific interactions. The presence of the conserved and tailored Z-DNA-binding surface, which interacts specifically with the zigzag backbone and syn base diagnostic of the Z-form, reinforces the importance to poxvirus infection of the ability of this protein to recognize the Z-conformation.
Figures


References
-
- Lee, H. J., Essani, K. & Smith, G. L. (2001) Virology 281, 170-192. - PubMed
-
- Whittaker, D. & Glaister, J. R. (1985) Lab. Anim. 19, 177-179. - PubMed
-
- Schielke, J. E., Kalishman, J., Liggitt, D. & Bielefeldt-Ohmann, H. (2002) Contemp. Top. Lab. Anim. Sci. 41, 27-29. - PubMed
-
- Rouhandeh, H., Vafai, A. & Kilpatrick, D. (1984) J. Ultrastruct. Res. 86, 100-105. - PubMed
-
- Knight, J. C., Novembre, F. J., Brown, D. R., Goldsmith, C. S. & Esposito, J. J. (1989) Virology 172, 116-124. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

