Rituximab induces different but overlapping sets of genes in human B-lymphoma cell lines
- PMID: 15449038
- PMCID: PMC11032865
- DOI: 10.1007/s00262-004-0599-4
Rituximab induces different but overlapping sets of genes in human B-lymphoma cell lines
Abstract
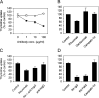
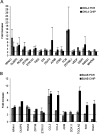
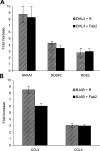
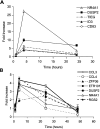
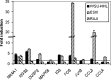
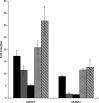
The therapeutic unconjugated anti-CD20 Mab rituximab is used for the treatment of B-non-Hodgkin's lymphomas. We have studied the direct biological effects, signalling and gene expression profiles induced by rituximab in two human B-lymphoma cell lines, DHL4 and BJAB, using microarray, quantitative PCR and gel shift analysis. Rituximab alone inhibited thymidine uptake and induced homotypic adhesion in DHL4 only, but not BJAB. Analysis of Affymetrix microchips carrying probes for about 10,000 human cDNAs, allowed us to identify 16 genes in DHL4 and 12 in BJAB induced by rituximab at 4 h. Eleven and seven of these genes were specific for DHL4 and BJAB, respectively; whereas the remaining five were up-regulated in both cell lines. Mean induction ranged from 2- to 16-fold. Real time PCR analysis allowed us to confirm up-regulation of all genes identified, except one in BJAB. Time course of induction of eight genes was studied, showing peak induction in most cases at 4 h. The up-regulation of 5/5 genes was also observed with the F(ab')(2) fragment of rituximab. Analysis of three further B-cell lymphoma lines showed that gene induction is not restricted to BJAB and DHL4. Finally, we show that rituximab alone can induce AP1 activation in both cell lines and provide evidence that the ERK1/2 pathway is involved in the rituximab-mediated up-regulation of gene expression. These data demonstrate that rituximab alone has direct signalling capacity in different B-lymphoma lines, inducing distinct but overlapping sets of genes which may play a role in the biological and/or therapeutic effect of the antibody.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Binding to CD20 by anti-B1 antibody or F(ab')(2) is sufficient for induction of apoptosis in B-cell lines.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2002 Mar;51(1):15-24. doi: 10.1007/s00262-001-0247-1. Epub 2001 Dec 18. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2002. PMID: 11845256 Free PMC article.
-
Rituximab (chimeric anti-CD20) sensitizes B-NHL cell lines to Fas-induced apoptosis.Oncogene. 2005 Dec 8;24(55):8114-27. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1208954. Oncogene. 2005. PMID: 16103877
-
Anti-CD20 antibody (IDEC-C2B8, rituximab) enhances efficacy of cytotoxic drugs on neoplastic lymphocytes in vitro: role of cytokines, complement, and caspases.Haematologica. 2002 Jan;87(1):33-43. Haematologica. 2002. PMID: 11801463
-
Rituximab: a review of its use in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma and chronic lymphocytic leukaemia.Drugs. 2003;63(8):803-43. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200363080-00005. Drugs. 2003. PMID: 12662126 Review.
-
Cellular and molecular signal transduction pathways modulated by rituximab (rituxan, anti-CD20 mAb) in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma: implications in chemosensitization and therapeutic intervention.Oncogene. 2005 Mar 24;24(13):2121-43. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1208349. Oncogene. 2005. PMID: 15789036 Review.
Cited by
-
Cholesterol depletion inhibits src family kinase-dependent calcium mobilization and apoptosis induced by rituximab crosslinking.Immunology. 2005 Oct;116(2):223-32. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2005.02213.x. Immunology. 2005. PMID: 16162271 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of Rituximab therapy on the chromosomes of patients with Rheumatoid arthritis.Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 2010 May;10(2):121-4. doi: 10.17305/bjbms.2010.2706. Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 2010. PMID: 20507292 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Protective effects of rituximab on puromycin-induced apoptosis, loss of adhesion and cytoskeletal alterations in human podocytes.Sci Rep. 2022 Jul 19;12(1):12297. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-16333-w. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35853959 Free PMC article.
-
γδ T-cell killing of primary follicular lymphoma cells is dramatically potentiated by GA101, a type II glycoengineered anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody.Haematologica. 2011 Mar;96(3):400-7. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2010.029520. Epub 2010 Nov 25. Haematologica. 2011. PMID: 21109686 Free PMC article.
-
Rituximab targets podocytes in recurrent focal segmental glomerulosclerosis.Sci Transl Med. 2011 Jun 1;3(85):85ra46. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3002231. Sci Transl Med. 2011. PMID: 21632984 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bustin SA, Nie XF, Barnard RC, JKumar V, Pascall JC, Brown KD, Leigh IM, Williams NS, McKay IA. Cloning and characterisation of ERF-1, a human member of the Tis11 family of early-response genes. DNA Cell Biol. 1994;13:449–459. - PubMed
-
- Chan HT, Hughes D, French RR, Tutt AL, Walshe CA, Teeling JL, Glennie MJ, Cragg MS. CD20-induced lymphoma cell death is independent of both caspases and its redistribution into triton X-100 insoluble membrane rafts. Cancer Res. 2003;63:5480–5489. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

