A comprehensive evaluation of food fortification with folic acid for the primary prevention of neural tube defects
- PMID: 15450123
- PMCID: PMC524178
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2393-4-20
A comprehensive evaluation of food fortification with folic acid for the primary prevention of neural tube defects
Abstract
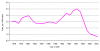
BACKGROUND: Periconceptional use of vitamin supplements containing folic acid reduces the risk of a neural tube defect (NTD). In November 1998, food fortification with folic acid was mandated in Canada, as a public health strategy to increase the folic acid intake of all women of childbearing age. We undertook a comprehensive population based study in Newfoundland to assess the benefits and possible adverse effects of this intervention. METHODS: This study was carried out in women aged 19-44 years and in seniors from November 1997 to March 1998, and from November 2000 to March 2001. The evaluation was comprised of four components: I) Determination of rates of NTDs; II) Dietary assessment; III) Blood analysis; IV) Assessment of knowledge and use of folic acid supplements. RESULTS: The annual rates of NTDs in Newfoundland varied greatly between 1976 and 1997, with a mean rate of 3.40 per 1,000 births. There was no significant change in the average rates between 1991-93 and 1994-97 (relative risk [RR] 1.01, 95% confidence interval [CI] 0.76-1.34). The rates of NTDs fell by 78% (95% CI 65%-86%) after the implementation of folic acid fortification, from an average of 4.36 per 1,000 births during 1991-1997 to 0.96 per 1,000 births during 1998-2001 (RR 0.22, 95% CI 0.14-0.35). The average dietary intake of folic acid due to fortification was 70 μg/day in women aged 19-44 years and 74 μg/day in seniors. There were significant increases in serum and RBC folate levels for women and seniors after mandatory fortification. Among seniors, there were no significant changes in indices typical of vitamin B12 deficiencies, and no evidence of improved folate status masking haematological manifestations of vitamin B12 deficiency. The proportion of women aged 19-44 years taking a vitamin supplement containing folic acid increased from 17% to 28%. CONCLUSIONS: Based on these findings, mandatory food fortification in Canada should continue at the current levels. Public education regarding folic acid supplement use by women of childbearing age should also continue.
Figures
References
-
- Health Canada Canadian Perinatal Health Report 2000. Ottawa: Minister of Public Works and Government Services Canada. 2000.
-
- Crane JMG, Sun C, Hutchens D, Crowley M. The epidemiology of neural tube defects in Newfoundland and Labrador. J Soc Obstet Gynaecol Can. 2001;23:510–514.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources