RANKL-induced DC-STAMP is essential for osteoclastogenesis
- PMID: 15452179
- PMCID: PMC2213286
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20040518
RANKL-induced DC-STAMP is essential for osteoclastogenesis
Abstract
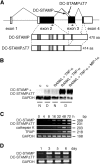
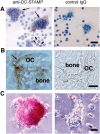
Osteoclasts are bone-resorbing, multinucleated giant cells that are essential for bone remodeling and are formed through cell fusion of mononuclear precursor cells. Although receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappaB ligand (RANKL) has been demonstrated to be an important osteoclastogenic cytokine, the cell surface molecules involved in osteoclastogenesis are mostly unknown. Here, we report that the seven-transmembrane receptor-like molecule, dendritic cell-specific transmembrane protein (DC-STAMP) is involved in osteoclastogenesis. Expression of DC-STAMP is rapidly induced in osteoclast precursor cells by RANKL and other osteoclastogenic stimulations. Targeted inhibition of DC-STAMP by small interfering RNAs and specific antibody markedly suppressed the formation of multinucleated osteoclast-like cells. Overexpression of DC-STAMP enhanced osteoclastogenesis in the presence of RANKL. Furthermore, DC-STAMP directly induced the expression of the osteoclast marker tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase. These data demonstrate for the first time that DC-STAMP has an essential role in osteoclastogenesis.
Figures
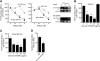
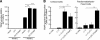
References
-
- Roodman, G.D. 1999. Cell biology of the osteoclast. Exp. Hematol. 27:1229–1241. - PubMed
-
- Suda, T., N. Takahashi, N. Udagawa, E. Jimi, M.T. Gillespie, and T.J. Martin. 1999. Modulation of osteoclast differentiation and function by the new members of the tumor necrosis factor receptor and ligand families. Endocr. Rev. 20:345–357. - PubMed
-
- Boyle, W.J., W.S. Simonet, and D.L. Lacey. 2003. Osteoclast differentiation and activation. Nature. 423:337–342. - PubMed
-
- Teitelbaum, S.L., and F.P. Ross. 2003. Genetic regulation of osteoclast development and function. Nat. Rev. Genet. 4:638–649. - PubMed
-
- Han, X., H. Sterling, Y. Chen, C. Saginario, E.J. Brown, W.A. Frazier, F.P. Lindberg, and A. Vignery. 2000. CD47, a ligand for the macrophage fusion receptor, participates in macrophage multinucleation. J. Biol. Chem. 275:37984–37992. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

