LMP2A does not require palmitoylation to localize to buoyant complexes or for function
- PMID: 15452208
- PMCID: PMC521828
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.78.20.10878-10887.2004
LMP2A does not require palmitoylation to localize to buoyant complexes or for function
Abstract
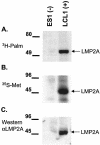
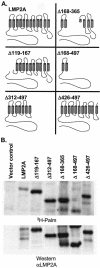
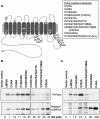
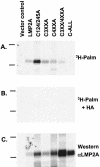
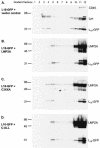
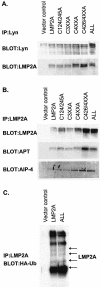
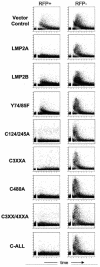
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) latent membrane protein 2A (LMP2A) is expressed constitutively in lipid rafts in latently infected B lymphocytes. Lipid rafts are membrane microdomains enriched in cholesterol and sphingolipids selective for specific protein association. Lipid rafts have been shown to be necessary for B-cell receptor (BCR) signal transduction. LMP2A prevents BCR recruitment to lipid rafts, thereby abrogating BCR function. As LMP2A is palmitoylated, whether this fatty acid modification is necessary for LMP2A to localize to lipid rafts and for protein function was investigated. LMP2A palmitoylation was confirmed in latently infected B cells. LMP2A was found to be palmitoylated on multiple cysteines only by S acylation. An LMP2A mutant that was not palmitoylated was identified and functioned similar to wild-type LMP2A; unmodified LMP2A localized to lipid rafts, was tyrosine phosphorylated, was associated with LMP2A-associated proteins, was ubiquitinated, and was able to block calcium mobilization following BCR cross-linking. Therefore, palmitoylation of LMP2A is not required for LMP2A targeting to buoyant complexes or for function.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tyrosines 60, 64, and 101 of Epstein-Barr virus LMP2A are not essential for blocking B cell signal transduction.Virology. 1999 Oct 25;263(2):485-95. doi: 10.1006/viro.1999.9964. Virology. 1999. PMID: 10544120
-
Epstein-Barr virus coopts lipid rafts to block the signaling and antigen transport functions of the BCR.Immunity. 2001 Jan;14(1):57-67. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(01)00089-9. Immunity. 2001. PMID: 11163230
-
Tyrosine 112 of latent membrane protein 2A is essential for protein tyrosine kinase loading and regulation of Epstein-Barr virus latency.J Virol. 1998 Oct;72(10):7796-806. doi: 10.1128/JVI.72.10.7796-7806.1998. J Virol. 1998. PMID: 9733815 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of the Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 2A on B cell function.Int Rev Immunol. 2001;20(6):805-35. doi: 10.3109/08830180109045591. Int Rev Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11913951 Review.
-
Latent Membrane Protein 2 (LMP2).Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2015;391:151-80. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-22834-1_5. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26428374 Review.
Cited by
-
Cholesterol is critical for Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 2A trafficking and protein stability.Virology. 2007 Apr 10;360(2):461-8. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2006.10.046. Epub 2006 Dec 5. Virology. 2007. PMID: 17150237 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-barr virus latent membrane protein 2B (LMP2B) modulates LMP2A activity.J Virol. 2007 Jan;81(1):84-94. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01302-06. Epub 2006 Oct 11. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17035319 Free PMC article.
-
Viral modulation of T-cell receptor signaling.J Virol. 2008 May;82(9):4194-204. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00059-08. Epub 2008 Feb 20. J Virol. 2008. PMID: 18287237 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Functional diversity: update of the posttranslational modification of Epstein-Barr virus coding proteins.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022 Nov 14;79(12):590. doi: 10.1007/s00018-022-04561-2. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022. PMID: 36376593 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Masters of manipulation: Viral modulation of the immunological synapse.Cell Microbiol. 2018 Oct;20(10):e12944. doi: 10.1111/cmi.12944. Cell Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30123959 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bijlmakers, M. J., and M. Marsh. 2003. The on-off story of protein palmitoylation. Trends Cell Biol. 13:32-42. - PubMed
-
- Brown, D. A., and K. Jacobson. 2001. Microdomains, lipid rafts and caveolae (San Feliu de Guixols, Spain, 19-24 May 2001). Traffic 2:668-672. - PubMed
-
- Brown, D. A., and E. London. 1998. Structure and origin of ordered lipid domains in biological membranes. J. Membr. Biol. 164:103-114. - PubMed
-
- Brown, D. A., and J. K. Rose. 1992. Sorting of GPI-anchored proteins to glycolipid-enriched membrane subdomains during transport to the apical cell surface. Cell 68:533-544. - PubMed
-
- Caldwell, R. G., J. B. Wilson, S. J. Anderson, and R. Longnecker. 1998. Epstein-Barr virus LMP2A drives B cell development and survival in the absence of normal B cell receptor signals. Immunity 9:405-411. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

