Phosphatidylserine is not the cell surface receptor for vesicular stomatitis virus
- PMID: 15452212
- PMCID: PMC521854
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.78.20.10920-10926.2004
Phosphatidylserine is not the cell surface receptor for vesicular stomatitis virus
Abstract
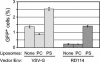
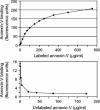
The envelope protein from vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) has become an important tool for gene transfer and gene therapy. It is widely used mainly because of its ability to mediate virus entry into all cell types tested to date. Consistent with the broad tropism of the virus, the receptor for VSV is thought to be a ubiquitous membrane lipid, phosphatidylserine (PS). However, the evidence for this hypothesis is indirect and incomplete. Here, we have examined the potential interaction of VSV and PS at the plasma membrane in more detail. Measurements of cell surface levels of PS show a wide range across cell types from different organisms. We demonstrate that there is no correlation between the cell surface PS levels and VSV infection or binding. We also demonstrate that an excess of annexin V, which binds specifically and tightly to PS, does not inhibit infection or binding by VSV. While the addition of PS to cells does allow increased virus entry, we show that this effect is not specific to the VSV envelope. We conclude that PS is not the cell surface receptor for VSV, although it may be involved in a postbinding step of virus entry.
Figures



References
-
- Andree, H. A., C. P. Reutelingsperger, R. Hauptmann, H. C. Hemker, W. T. Hermens, and G. M. Willems. 1990. Binding of vascular anticoagulant alpha (VAC alpha) to planar phospholipid bilayers. J. Biol. Chem. 265:4923-4928. - PubMed
-
- Bartz, S. R., and M. A. Vodicka. 1997. Production of high-titer human immunodeficiency virus type 1 pseudotyped with vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein. Methods 12:337-342. - PubMed
-
- Boon, J. M., and B. D. Smith. 2002. Chemical control of phospholipid distribution across bilayer membranes. Med. Res. Rev. 22:251-281. - PubMed
-
- Callahan, M. K., P. Williamson, and R. A. Schlegel. 2000. Surface expression of phosphatidylserine on macrophages is required for phagocytosis of apoptotic thymocytes. Cell Death Differ. 7:645-653. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

