A lentiviral cDNA library employing lambda recombination used to clone an inhibitor of human immunodeficiency virus type 1-induced cell death
- PMID: 15452256
- PMCID: PMC521860
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.78.20.11352-11359.2004
A lentiviral cDNA library employing lambda recombination used to clone an inhibitor of human immunodeficiency virus type 1-induced cell death
Abstract
Expression cloning technology of cDNAs is a suitable tool for identifying novel functional properties of genes. Here, we generated a lentiviral cDNA library-expressing system for human T cells based on a site-specific recombination system of phage lambda for transferring cDNA libraries with a minimum loss of its complexity. The library-transduced CD4(+) T cells were challenged with wild-type human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1), and the cells that acquired resistance to HIV-1-induced cytopathic effect (CPE) were selected. From these cells, CD14 was isolated and proved to inhibit the entry of HIV-1 and the HIV-1-induced CPE. This cloning system allows rapid identification of genes encoding novel properties in human T cells and probably other mammalian cells.
Figures
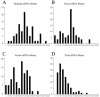
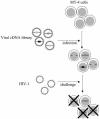




Similar articles
-
Inhibition of simian/human immunodeficiency virus replication in CD4+ T cells derived from lentiviral-transduced CD34+ hematopoietic cells.Mol Ther. 2005 Dec;12(6):1157-67. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2005.07.698. Epub 2005 Sep 15. Mol Ther. 2005. PMID: 16168713
-
Generation of a packaging cell line for prolonged large-scale production of high-titer HIV-1-based lentiviral vector.J Gene Med. 2005 Jun;7(6):818-34. doi: 10.1002/jgm.726. J Gene Med. 2005. PMID: 15693055
-
Lentiviral siRNAs targeting multiple highly conserved RNA sequences of human immunodeficiency virus type 1.Gene Ther. 2005 Jul;12(14):1133-44. doi: 10.1038/sj.gt.3302509. Gene Ther. 2005. PMID: 15750613
-
Construction of cDNA libraries in vaccinia virus.Methods Mol Biol. 2004;269:65-76. doi: 10.1385/1-59259-789-0:065. Methods Mol Biol. 2004. PMID: 15114008 Review.
-
[Construction of libraries of structural genes (cDNA) and "jumping" gene libraries in lambda vectors].Mol Biol (Mosk). 1989 Sep-Oct;23(5):1205-20. Mol Biol (Mosk). 1989. PMID: 2532708 Review. Russian.
Cited by
-
Modulation of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infectivity through incorporation of tetraspanin proteins.J Virol. 2008 Jan;82(2):1021-33. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01044-07. Epub 2007 Nov 7. J Virol. 2008. PMID: 17989173 Free PMC article.
-
A carboxy-terminally truncated human CPSF6 lacking residues encoded by exon 6 inhibits HIV-1 cDNA synthesis and promotes capsid disassembly.J Virol. 2013 Jul;87(13):7726-36. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00124-13. Epub 2013 May 8. J Virol. 2013. PMID: 23658440 Free PMC article.
-
CKIP-1 is an intrinsic negative regulator of T-cell activation through an interaction with CARMA1.PLoS One. 2014 Jan 17;9(1):e85762. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0085762. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24465689 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of RyDEN (C19orf66) as an Interferon-Stimulated Cellular Inhibitor against Dengue Virus Replication.PLoS Pathog. 2016 Jan 6;12(1):e1005357. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005357. eCollection 2016 Jan. PLoS Pathog. 2016. PMID: 26735137 Free PMC article.
-
Efficient transduction of cytotoxic and anti-HIV-1 genes by a gene-regulatable lentiviral vector.Virus Genes. 2009 Oct;39(2):165-75. doi: 10.1007/s11262-009-0382-x. Virus Genes. 2009. PMID: 19554442
References
-
- Case, S. S., M. A. Price, C. T. Jordan, X. J. Yu, L. Wang, G. Bauer, D. L. Haas, D. Xu, R. Stripecke, L. Naldini, D. B. Kohn, and G. M. Crooks. 1999. Stable transduction of quiescent CD34+CD38− human hematopoietic cells by HIV-1-based lentiviral vectors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96:2988-2993. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gartner, S., P. Markovits, D. M. Markovitz, M. H. Kaplan, R. C. Gallo, and M. Popovic. 1986. The role of mononuclear phagocytes in HTLV-III/LAV infection. Science 233:215-219. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

