Spatial memory, recognition memory, and the hippocampus
- PMID: 15452348
- PMCID: PMC521976
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0406344101
Spatial memory, recognition memory, and the hippocampus
Abstract
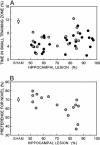
There is wide agreement that spatial memory is dependent on the integrity of the hippocampus, but the importance of the hippocampus for nonspatial tasks, including tasks of object recognition memory is not as clear. We examined the relationship between hippocampal lesion size and both spatial memory and object recognition memory in rats. Spatial memory was impaired after bilateral dorsal hippocampal lesions that encompassed 30-50% total volume, and as lesion size increased from 50% to approximately 100% of total hippocampal volume, performance was similarly impaired. In contrast, object recognition was intact after dorsal hippocampal lesions that damaged 50-75% of total hippocampal volume and was impaired only after larger lesions that encompassed 75-100% of hippocampal volume. Last, ventral hippocampal lesions that encompassed approximately 50% of total hippocampal volume impaired spatial memory but did not affect object recognition memory. These findings show that the hippocampus is important for both spatial memory and recognition memory. However, spatial memory performance requires more hippocampal tissue than does recognition memory.
Figures
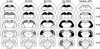
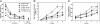
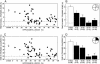
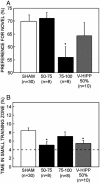
References
-
- Squire, L. R. (1992) Psychol. Rev. 99, 195-231. - PubMed
-
- Eichenbaum, H. & Cohen, N. J. (2001) From Conditioning to Conscious Recollection: Memory Systems of the Brain (Oxford Univ. Press, London).
-
- Suzuki, W. A. & Eichenbaum, H. (2000) Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 911, 175-191. - PubMed
-
- Squire, L. R., Stark, C. E. L. & Clark, R. E. (2004) Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 27, 279-306. - PubMed
-
- Fujimichi, R., Naya, Y. & Miyashita, Y. in Cognitive Neurosciences III, ed. Gazzaniga, M. S. (MIT Press, Cambridge, MA), in press.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

