Microarrays for global expression constructed with a low redundancy set of 27,500 sequenced cDNAs representing an array of developmental stages and physiological conditions of the soybean plant
- PMID: 15453914
- PMCID: PMC526184
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-5-73
Microarrays for global expression constructed with a low redundancy set of 27,500 sequenced cDNAs representing an array of developmental stages and physiological conditions of the soybean plant
Abstract
Background: Microarrays are an important tool with which to examine coordinated gene expression. Soybean (Glycine max) is one of the most economically valuable crop species in the world food supply. In order to accelerate both gene discovery as well as hypothesis-driven research in soybean, global expression resources needed to be developed. The applications of microarray for determining patterns of expression in different tissues or during conditional treatments by dual labeling of the mRNAs are unlimited. In addition, discovery of the molecular basis of traits through examination of naturally occurring variation in hundreds of mutant lines could be enhanced by the construction and use of soybean cDNA microarrays.
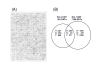
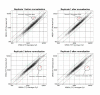
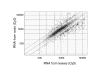
Results: We report the construction and analysis of a low redundancy 'unigene' set of 27,513 clones that represent a variety of soybean cDNA libraries made from a wide array of source tissue and organ systems, developmental stages, and stress or pathogen-challenged plants. The set was assembled from the 5' sequence data of the cDNA clones using cluster analysis programs. The selected clones were then physically reracked and sequenced at the 3' end. In order to increase gene discovery from immature cotyledon libraries that contain abundant mRNAs representing storage protein gene families, we utilized a high density filter normalization approach to preferentially select more weakly expressed cDNAs. All 27,513 cDNA inserts were amplified by polymerase chain reaction. The amplified products, along with some repetitively spotted control or 'choice' clones, were used to produce three 9,728-element microarrays that have been used to examine tissue specific gene expression and global expression in mutant isolines.
Conclusions: Global expression studies will be greatly aided by the availability of the sequence-validated and low redundancy cDNA sets described in this report. These cDNAs and ESTs represent a wide array of developmental stages and physiological conditions of the soybean plant. We also demonstrate that the quality of the data from the soybean cDNA microarrays is sufficiently reliable to examine isogenic lines that differ with respect to a mutant phenotype and thereby to define a small list of candidate genes potentially encoding or modulated by the mutant phenotype.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Specific elements of the glyoxylate pathway play a significant role in the functional transition of the soybean cotyledon during seedling development.BMC Genomics. 2007 Dec 19;8:468. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-8-468. BMC Genomics. 2007. PMID: 18093333 Free PMC article.
-
Microarray analysis of iron deficiency chlorosis in near-isogenic soybean lines.BMC Genomics. 2007 Dec 21;8:476. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-8-476. BMC Genomics. 2007. PMID: 18154662 Free PMC article.
-
Sequencing and analysis of approximately 40,000 soybean cDNA clones from a full-length-enriched cDNA library.DNA Res. 2008 Dec;15(6):333-46. doi: 10.1093/dnares/dsn024. Epub 2008 Oct 16. DNA Res. 2008. PMID: 18927222 Free PMC article.
-
RIKEN Arabidopsis full-length (RAFL) cDNA and its applications for expression profiling under abiotic stress conditions.J Exp Bot. 2004 Jan;55(395):213-23. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erh007. Epub 2003 Dec 12. J Exp Bot. 2004. PMID: 14673034 Review.
-
Disease profiling arrays: reverse format cDNA arrays complimentary to microarrays.Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol. 2004;86:191-213. doi: 10.1007/b12443. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol. 2004. PMID: 15088766 Review.
Cited by
-
Transcriptome analysis reveals a critical role of CHS7 and CHS8 genes for isoflavonoid synthesis in soybean seeds.Plant Physiol. 2007 Jan;143(1):326-38. doi: 10.1104/pp.106.086306. Epub 2006 Nov 10. Plant Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17098860 Free PMC article.
-
Specific elements of the glyoxylate pathway play a significant role in the functional transition of the soybean cotyledon during seedling development.BMC Genomics. 2007 Dec 19;8:468. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-8-468. BMC Genomics. 2007. PMID: 18093333 Free PMC article.
-
Functional genomics of soybean for improvement of productivity in adverse conditions.Funct Integr Genomics. 2010 Nov;10(4):447-62. doi: 10.1007/s10142-010-0178-z. Epub 2010 Jun 27. Funct Integr Genomics. 2010. PMID: 20582712 Review.
-
Genomic evaluation of oxalate-degrading transgenic soybean in response to Sclerotinia sclerotiorum infection.Mol Plant Pathol. 2014 Aug;15(6):563-75. doi: 10.1111/mpp.12115. Epub 2014 Apr 10. Mol Plant Pathol. 2014. PMID: 24382019 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of regulatory networks and hub genes controlling soybean seed set and size using RNA sequencing analysis.J Exp Bot. 2017 Apr 1;68(8):1955-1972. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erw460. J Exp Bot. 2017. PMID: 28087653 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Velculescu VE, Ahang L, Vogelstein B, Kinzler KW. Serial analysis of gene expression. Science. 1995;270:484–487. - PubMed
-
- Shoemaker R, Keim P, Vodkin L, Retzel E, Clifton SW, Waterston , Smoller D, Coryell V, Khanna A, Erpelding J, Gai X, Brendel V, Raph-Schmidt C, Shoop EG, Vielweber CJ, Schmatz M, Pape D, Bowers Y, Theising B, Martin J, Dante M, Wylie T, Granger C. A compilation of soybean ESTs: generation and analysis. Genome. 2002;45:329–338. doi: 10.1139/g01-150. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

