Spinal dorsal horn calcium channel alpha2delta-1 subunit upregulation contributes to peripheral nerve injury-induced tactile allodynia
- PMID: 15456823
- PMCID: PMC1635787
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2982-04.2004
Spinal dorsal horn calcium channel alpha2delta-1 subunit upregulation contributes to peripheral nerve injury-induced tactile allodynia
Abstract
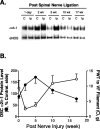
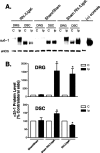
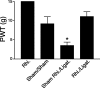
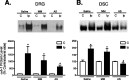
Peripheral nerve injury induces upregulation of the calcium channel alpha2delta-1 structural subunit in dorsal root ganglia (DRG) and dorsal spinal cord of spinal nerve-ligated rats with neuropathic pain, suggesting a role of the calcium channel alpha2delta-1 subunit in central sensitization. To investigate whether spinal dorsal horn alpha2delta-1 subunit upregulation derives from increased DRG alpha2delta-1 subunit and plays a causal role in neuropathic pain development, we examined spinal dorsal hornalpha2delta-1 subunit expression with or without dorsal rhizotomy in spinal nerve-ligated rats and its correlation with tactile allodynia, a neuropathic pain state defined as reduced thresholds to non-noxious tactile stimulation. We also examined the effects of intrathecal alpha2delta-1 antisense oligonucleotides on alpha2delta-1 subunit expression and neuropathic allodynia in the nerve-ligated rats. Our data indicated that spinal nerve injury resulted in time-dependentalpha2delta-1 subunit upregulation in the spinal dorsal horn that correlated temporally with neuropathic allodynia development and maintenance. Dorsal rhizotomy diminished basal level expression and blocked injury-induced expression of the spinal dorsal hornalpha2delta-1 subunit and reversed injury-induced tactile allodynia. In addition, intrathecal alpha2delta-1 antisense oligonucleotides blocked injury-induced dorsal horn alpha2delta-1 subunit upregulation and diminished tactile allodynia. These findings indicate that alpha2delta-1 subunit basal expression occurs presynaptically and postsynaptically in spinal dorsal horn. Nerve injury induces mainly presynaptic alpha2delta-1 subunit expression that derives from increased alpha2delta-1 subunit in injured DRG neurons. Thus, changes in presynaptic alpha2delta-1 subunit expression contribute to injury-induced spinal neuroplasticity and central sensitization that underlies neuropathic pain development and maintenance.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Upregulation of calcium channel alpha-2-delta-1 subunit in dorsal horn contributes to spinal cord injury-induced tactile allodynia.Spine J. 2018 Jun;18(6):1062-1069. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2018.01.010. Epub 2018 Jan 31. Spine J. 2018. PMID: 29355786
-
Calcium channel alpha-2-delta-1 protein upregulation in dorsal spinal cord mediates spinal cord injury-induced neuropathic pain states.Pain. 2011 Mar;152(3):649-655. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2010.12.014. Epub 2011 Jan 15. Pain. 2011. PMID: 21239111 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulation of dorsal root ganglion (alpha)2(delta) calcium channel subunit and its correlation with allodynia in spinal nerve-injured rats.J Neurosci. 2001 Mar 15;21(6):1868-75. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-06-01868.2001. J Neurosci. 2001. PMID: 11245671 Free PMC article.
-
Presynaptic NMDA receptors control nociceptive transmission at the spinal cord level in neuropathic pain.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019 May;76(10):1889-1899. doi: 10.1007/s00018-019-03047-y. Epub 2019 Feb 20. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 30788514 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of the immune system in neuropathic pain.Scand J Pain. 2019 Dec 18;20(1):33-37. doi: 10.1515/sjpain-2019-0138. Scand J Pain. 2019. PMID: 31730538 Review.
Cited by
-
Spinal 5-HT3 receptors facilitate behavioural hypersensitivity induced by elevated calcium channel alpha-2-delta-1 protein.Eur J Pain. 2013 Apr;17(4):505-13. doi: 10.1002/j.1532-2149.2012.00221.x. Epub 2012 Oct 12. Eur J Pain. 2013. PMID: 23065867 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular basis for the dosing time-dependency of anti-allodynic effects of gabapentin in a mouse model of neuropathic pain.Mol Pain. 2010 Nov 26;6:83. doi: 10.1186/1744-8069-6-83. Mol Pain. 2010. PMID: 21108841 Free PMC article.
-
The α2δ-1-NMDA Receptor Complex Is Critically Involved in Neuropathic Pain Development and Gabapentin Therapeutic Actions.Cell Rep. 2018 Feb 27;22(9):2307-2321. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.02.021. Cell Rep. 2018. PMID: 29490268 Free PMC article.
-
Differential effects of voltage-gated calcium channel blockers on calcium channel alpha-2-delta-1 subunit protein-mediated nociception.Eur J Pain. 2015 May;19(5):639-48. doi: 10.1002/ejp.585. Epub 2014 Aug 27. Eur J Pain. 2015. PMID: 25158907 Free PMC article.
-
Thrombospondins and synaptogenesis.Neural Regen Res. 2012 Aug 5;7(22):1737-43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5374.2012.22.009. Neural Regen Res. 2012. PMID: 25624796 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ahlijanian MK, Westenbroek RE, Catterall WA (1990) Subunit structure and localization of dihydropyridine-sensitive calcium channels in mammalian brain, spinal cord, and retina. Neuron 4: 819-832. - PubMed
-
- Brust PF, Simerson S, McCue AF, Deal CR, Schoonmaker S, Williams ME, Veliçelebi G, Johnson EC, Harpold MM, Ellis SB (1993) Human neuronal voltage-dependent calcium channels: studies on subunit structure and role in channel assembly. Neuropharmacology 32: 1089-1102. - PubMed
-
- Chaplan SR, Bach FW, Pogrel JW, Chung JM, Yaksh TL (1994) Quantitative assessment of tactile allodynia in the rat paw. J Neurosci Methods 53: 55-63. - PubMed
-
- Coull JA, Boudreau D, Bachand K, Prescott SA, Nault F, Sik A, De Koninck P, De Koninck Y (2003) Trans-synaptic shift in anion gradient in spinal lamina I neurons as a mechanism of neuropathic pain. Nature 424: 938-942. - PubMed
-
- De Jongh KS, Warner C, Catterall WA (1990) Subunits of purified calcium channels. α2 and δ are encoded by the same gene. J Biol Chem 265: 14738-14741. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
