Artemis is a phosphorylation target of ATM and ATR and is involved in the G2/M DNA damage checkpoint response
- PMID: 15456891
- PMCID: PMC517881
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.24.20.9207-9220.2004
Artemis is a phosphorylation target of ATM and ATR and is involved in the G2/M DNA damage checkpoint response
Abstract
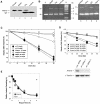
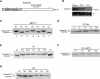
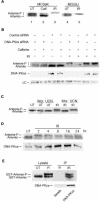
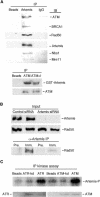
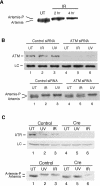
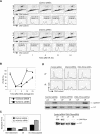
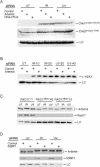
Mutations in Artemis in both humans and mice result in severe combined immunodeficiency due to a defect in V(D)J recombination. In addition, Artemis mutants are radiosensitive and chromosomally unstable, which has been attributed to a defect in nonhomologous end joining (NHEJ). We show here, however, that Artemis-depleted cell extracts are not defective in NHEJ and that Artemis-deficient cells have normal repair kinetics of double-strand breaks after exposure to ionizing radiation (IR). Artemis is shown, however, to interact with known cell cycle checkpoint proteins and to be a phosphorylation target of the checkpoint kinase ATM or ATR after exposure of cells to IR or UV irradiation, respectively. Consistent with these findings, our results also show that Artemis is required for the maintenance of a normal DNA damage-induced G2/M cell cycle arrest. Artemis does not appear, however, to act either upstream or downstream of checkpoint kinase Chk1 or Chk2. These results define Artemis as having a checkpoint function and suggest that the radiosensitivity and chromosomal instability of Artemis-deficient cells may be due to defects in cell cycle responses after DNA damage.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of ATM and the damage response mediator proteins 53BP1 and MDC1 in the maintenance of G(2)/M checkpoint arrest.Mol Cell Biol. 2010 Jul;30(13):3371-83. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01644-09. Epub 2010 Apr 26. Mol Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20421415 Free PMC article.
-
An imperfect G2M checkpoint contributes to chromosome instability following irradiation of S and G2 phase cells.Cell Cycle. 2007 Jul 15;6(14):1682-6. doi: 10.4161/cc.6.14.4480. Epub 2007 May 21. Cell Cycle. 2007. PMID: 17637566 Review.
-
Artemis links ATM to G2/M checkpoint recovery via regulation of Cdk1-cyclin B.Mol Cell Biol. 2007 Apr;27(7):2625-35. doi: 10.1128/MCB.02072-06. Epub 2007 Jan 22. Mol Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17242184 Free PMC article.
-
Irradiation-induced G2/M checkpoint response requires ERK1/2 activation.Oncogene. 2007 Jul 12;26(32):4689-98. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1210268. Epub 2007 Feb 5. Oncogene. 2007. PMID: 17297454
-
The influence of heterochromatin on DNA double strand break repair: Getting the strong, silent type to relax.DNA Repair (Amst). 2010 Dec 10;9(12):1273-82. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2010.09.013. Epub 2010 Oct 30. DNA Repair (Amst). 2010. PMID: 21036673 Review.
Cited by
-
In silico identification and analysis of new Artemis/Artemis-like sequences from fungal and metazoan species.Protein J. 2005 Aug;24(6):399-411. doi: 10.1007/s10930-005-7594-2. Protein J. 2005. PMID: 16323046
-
Replication independent DNA double-strand break retention may prevent genomic instability.Mol Cancer. 2010 Mar 31;9:70. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-9-70. Mol Cancer. 2010. PMID: 20356374 Free PMC article.
-
Non-homologous end joining: emerging themes and unanswered questions.DNA Repair (Amst). 2014 May;17:2-8. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2014.01.009. Epub 2014 Feb 26. DNA Repair (Amst). 2014. PMID: 24582502 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Artemis regulates cell cycle recovery from the S phase checkpoint by promoting degradation of cyclin E.J Biol Chem. 2009 Jul 3;284(27):18236-43. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.002584. Epub 2009 May 7. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19423708 Free PMC article.
-
Snm1B/Apollo mediates replication fork collapse and S Phase checkpoint activation in response to DNA interstrand cross-links.Oncogene. 2008 Aug 28;27(37):5045-56. doi: 10.1038/onc.2008.139. Epub 2008 May 12. Oncogene. 2008. PMID: 18469862 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abraham, R. T. 2001. Cell cycle checkpoints signaling through the ATM and ATR kinases. Genes Dev. 15:2177-2196. - PubMed
-
- Allalunis-Turner, J., G. M. Barron, and R. S. Day III. 1997. Intact G2-phase checkpoint in cells of a human cell line lacking DNA-dependent protein kinase activity. Radiat. Res. 147:284-287. - PubMed
-
- Banin, S., L. Moyal, S. Shieh, Y. Taya, C. W. Anderson, L. Chessa, N. I. Smorodinsky, C. Prives, Y. Reiss, Y. Shiloh, and Y. Ziv. 1998. Enhanced phosphorylation of p53 by ATM in response to DNA damage. Science 281:1674-1677. - PubMed
-
- Bao, S., R. S. Tibbetts, K. M. Brumbaugh, Y. Fang, D. A. Richardson, A. Ali, S. M. Chen, R. T. Abraham, and X. F. Wang. 2001. ATR/ATM-mediated phosphorylation of human Rad17 is required for genotoxic stress responses. Nature 411:969-974. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
