Mutational analysis of the N-terminal DNA-binding domain of sleeping beauty transposase: critical residues for DNA binding and hyperactivity in mammalian cells
- PMID: 15456893
- PMCID: PMC517896
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.24.20.9239-9247.2004
Mutational analysis of the N-terminal DNA-binding domain of sleeping beauty transposase: critical residues for DNA binding and hyperactivity in mammalian cells
Abstract
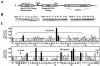
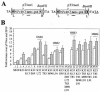
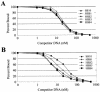
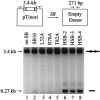
The N-terminal domain of the Sleeping Beauty (SB) transposase mediates transposon DNA binding, subunit multimerization, and nuclear translocation in vertebrate cells. For this report, we studied the relative contributions of 95 different residues within this multifunctional domain by large-scale mutational analysis. We found that each of four amino acids (leucine 25, arginine 36, isoleucine 42, and glycine 59) contributes to DNA binding in the context of the N-terminal 123 amino acids of SB transposase, as indicated by electrophoretic mobility shift analysis, and to functional activity of the full-length transposase, as determined by a quantitative HeLa cell-based transposition assay. Moreover, we show that amino acid substitutions within either the putative oligomerization domain (L11A, L18A, L25A, and L32A) or the nuclear localization signal (K104A and R105A) severely impair its ability to mediate DNA transposition in mammalian cells. In contrast, each of 10 single amino acid changes within the bipartite DNA-binding domain is shown to greatly enhance SB's transpositional activity in mammalian cells. These hyperactive mutations functioned synergistically when combined and are shown to significantly improve transposase affinity for transposon end sequences. Finally, we show that enhanced DNA-binding activity results in improved cleavage kinetics, increased SB element mobilization from host cell chromosomes, and dramatically improved gene transfer capabilities of SB in vivo in mice. These studies provide important insights into vertebrate transposon biology and indicate that Sleeping Beauty can be readily improved for enhanced genetic research applications in mammals.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Targeted Sleeping Beauty transposition in human cells.Mol Ther. 2007 Jun;15(6):1137-44. doi: 10.1038/sj.mt.6300169. Epub 2007 Apr 10. Mol Ther. 2007. PMID: 17426709
-
Counterselection and co-delivery of transposon and transposase functions for Sleeping Beauty-mediated transposition in cultured mammalian cells.Biosci Rep. 2004 Dec;24(6):577-94. doi: 10.1007/s10540-005-2793-9. Biosci Rep. 2004. PMID: 16158196
-
Development of hyperactive sleeping beauty transposon vectors by mutational analysis.Mol Ther. 2004 Feb;9(2):292-304. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2003.11.024. Mol Ther. 2004. PMID: 14759813
-
Sleeping Beauty Transposition.Microbiol Spectr. 2015 Apr;3(2):MDNA3-0042-2014. doi: 10.1128/microbiolspec.MDNA3-0042-2014. Microbiol Spectr. 2015. PMID: 26104705 Review.
-
The Sleeping Beauty transposon toolbox.Methods Mol Biol. 2012;859:229-40. doi: 10.1007/978-1-61779-603-6_13. Methods Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22367875 Review.
Cited by
-
Exogenous enzymes upgrade transgenesis and genetic engineering of farm animals.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015 May;72(10):1907-29. doi: 10.1007/s00018-015-1842-1. Epub 2015 Feb 1. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015. PMID: 25636347 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Generation of an inducible and optimized piggyBac transposon system.Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35(12):e87. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm446. Epub 2007 Jun 18. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007. PMID: 17576687 Free PMC article.
-
Affinities of Terminal Inverted Repeats to DNA Binding Domain of Transposase Affect the Transposition Activity of Bamboo Ppmar2 Mariner-Like Element.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jul 28;20(15):3692. doi: 10.3390/ijms20153692. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31357686 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct pathways of genomic progression to benign and malignant tumors of the liver.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Sep 11;104(37):14771-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0706578104. Epub 2007 Sep 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 17785413 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term reduction of jaundice in Gunn rats by nonviral liver-targeted delivery of Sleeping Beauty transposon.Hepatology. 2009 Sep;50(3):815-24. doi: 10.1002/hep.23060. Hepatology. 2009. PMID: 19585550 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cui, Z., A. M. Geurts, G. Liu, C. D. Kaufman, and P. B. Hackett. 2002. Structure-function analysis of the inverted terminal repeats of the sleeping beauty transposon. J. Mol. Biol. 318:1221-1235. - PubMed
-
- Drabek, D., L. Zagoraiou, T. deWit, A. Langeveld, C. Roumpaki, C. Mamalaki, C. Savakis, and F. Grosveld. 2003. Transposition of the Drosophila hydei Minos transposon in the mouse germ line. Genomics 81:108-111. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
