U1 RNA induces innate immunity signaling
- PMID: 15457457
- PMCID: PMC1475509
- DOI: 10.1002/art.20428
U1 RNA induces innate immunity signaling
Abstract
Objective: The U1-70-kd RNP is a prominent target of autoimmunity in connective tissue diseases. In this study, we explored whether its endogenous ligand, U1 RNA, mediates a proimmune signal and may be immunogenic.
Methods: We assayed the proliferation of control and MyD88-knockout splenocytes in response to in vitro-synthesized U1 RNA, and measured interleukin-6 (IL-6) and IL-8 secretion induced by U1 RNA in a human cell line competent for signaling through Toll-like receptor 3 (TLR-3) and TLR-5.
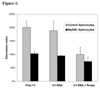
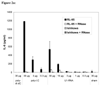
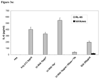
Results: Treatment with U1 RNA or with poly(I-C), a known agonist of TLR-3, induced approximately twice as much control splenocyte proliferation as did treatment with RNase-digested U1 RNA. Proliferation in response to either poly(I-C) or U1 RNA by MyD88-knockout splenocytes was similarly attenuated. Similar to poly(I-C), U1 RNA induced significant secretion of both IL-6 and IL-8 from a TLR-3-expressing human cell line; in contrast, the TLR-5 agonist flagellin induced predominantly IL-8 secretion. Pretreatment of U1 RNA with RNase abolished IL-6 and IL-8 secretion.
Conclusion: U1 RNA is capable of inducing manifestations consistent with TLR-3 activation. The ability of U1 RNA (which has a substantial double-stranded secondary structure) to activate TLR-3 may contribute to the immunogenicity of the U1-70-kd autoantigen. Stimulation of innate immunity by native RNA molecules with a double-stranded secondary structure may help explain the high prevalence of autoimmunity to RNA binding proteins.
Figures


References
-
- Sharp GC, Irvin WS, May CM, Holman HR, McDuffie FC, Hess EV, et al. Association of antibodies to ribonucleoprotein and Sm antigens with mixed connective-tissue disease, systematic lupus erythematosus and other rheumatic diseases. N Engl J Med. 1976;295:1149–54. - PubMed
-
- Greidinger EL, Hoffman RW. The appearance of U1 RNP antibody specificities in sequential autoimmune human antisera follows a characteristic order that implicates the U1–70 kd and B′/B proteins as predominant U1 RNP immunogens. Arthritis Rheum. 2001;44:368–75. - PubMed
-
- Reichlin M, Harley JB. Immune response to the RNA protein particles in systemic lupus erythematosus: a distinctive dichotomy. Am J Med. 1988;85:35–7. - PubMed
-
- Alexopoulou L, Holt AC, Medzhitov R, Flavell RA. Recognition of double-stranded RNA and activation of NF-κB by Toll-like receptor 3. Nature. 2001;413:732–8. - PubMed
-
- Lin WL, Pederson T. Ribonucleoprotein organization of eukaryotic RNA. XXXI. Structure of the U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein. J Mol Biol. 1984;180:947–60. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

