Distribution and dynamics of chromatin modification induced by a defined DNA double-strand break
- PMID: 15458641
- PMCID: PMC4493763
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2004.09.047
Distribution and dynamics of chromatin modification induced by a defined DNA double-strand break
Abstract
Background: In response to DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs), eukaryotic cells rapidly phosphorylate histone H2A isoform H2AX at a C-terminal serine (to form gamma-H2AX) and accumulate repair proteins at or near DSBs. To date, these events have been defined primarily at the resolution of light microscopes, and the relationship between gamma-H2AX formation and repair protein recruitment remains to be defined.
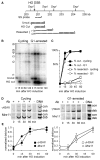
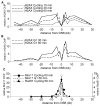
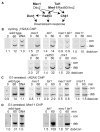
Results: We report here the first molecular-level characterization of regional chromatin changes that accompany a DSB formed by the HO endonuclease in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Break induction provoked rapid gamma-H2AX formation and equally rapid recruitment of the Mre11 repair protein. gamma-H2AX formation was efficiently promoted by both Tel1p and Mec1p, the yeast ATM and ATR homologs; in G1-arrested cells, most gamma-H2AX formation was dependent on Tel1 and Mre11. gamma-H2AX formed in a large (ca. 50 kb) region surrounding the DSB. Remarkably, very little gamma-H2AX could be detected in chromatin within 1-2 kb of the break. In contrast, this region contains almost all the Mre11p and other repair proteins that bind as a result of the break.
Conclusions: Both Mec1p and Tel1p can respond to a DSB, with distinct roles for these checkpoint kinases at different phases of the cell cycle. Part of this response involves histone phosphorylation over large chromosomal domains; however, the distinct distributions of gamma-H2AX and repair proteins near DSBs indicate that localization of repair proteins to breaks is not likely to be the main function of this histone modification.
Figures

Similar articles
-
DNA damage response pathway uses histone modification to assemble a double-strand break-specific cohesin domain.Mol Cell. 2004 Dec 22;16(6):991-1002. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2004.11.027. Mol Cell. 2004. PMID: 15610741
-
Yeast ATM and ATR kinases use different mechanisms to spread histone H2A phosphorylation around a DNA double-strand break.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Sep 1;117(35):21354-21363. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2002126117. Epub 2020 Aug 17. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32817543 Free PMC article.
-
Chromatin remodelling at a DNA double-strand break site in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Nature. 2005 Nov 17;438(7066):379-83. doi: 10.1038/nature04148. Nature. 2005. PMID: 16292314 Free PMC article.
-
GammaH2AX and its role in DNA double-strand break repair.Biochem Cell Biol. 2006 Aug;84(4):568-77. doi: 10.1139/o06-072. Biochem Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16936829 Review.
-
Chromatin modification and NBS1: their relationship in DNA double-strand break repair.Genes Genet Syst. 2016;90(4):195-208. doi: 10.1266/ggs.15-00010. Epub 2015 Nov 25. Genes Genet Syst. 2016. PMID: 26616756 Review.
Cited by
-
Caffeine impairs resection during DNA break repair by reducing the levels of nucleases Sae2 and Dna2.Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Aug 18;43(14):6889-901. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv520. Epub 2015 May 27. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. PMID: 26019182 Free PMC article.
-
Histone dosage regulates DNA damage sensitivity in a checkpoint-independent manner by the homologous recombination pathway.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Oct;40(19):9604-20. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks722. Epub 2012 Jul 31. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22850743 Free PMC article.
-
Overview for the histone codes for DNA repair.Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2012;110:207-27. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-387665-2.00008-0. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2012. PMID: 22749147 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A novel function for CDK2 activity at meiotic crossover sites.PLoS Biol. 2020 Oct 19;18(10):e3000903. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3000903. eCollection 2020 Oct. PLoS Biol. 2020. PMID: 33075054 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Nanog as a novel inhibitor of Rad51.Cell Death Dis. 2022 Feb 26;13(2):193. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-04644-9. Cell Death Dis. 2022. PMID: 35220392 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kurz EU, Lees-Miller SP. DNA damage-induced activation of ATM and ATM-dependent signaling pathways. DNA Repair (Amst) 2004;3:889–900. - PubMed
-
- Shechter D, Costanzo V, Gautier J. Regulation of DNA replication by ATR: signaling in response to DNA intermediates. DNA Repair (Amst) 2004;3:901–908. - PubMed
-
- Burma S, Chen DJ. Role of DNA-PK in the cellular response to DNA double-strand breaks. DNA Repair (Amst) 2004;3:909–918. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

