Voltage dependence of ATP-dependent K+ current in rat cardiac myocytes is affected by IK1 and IK(ACh)
- PMID: 15459245
- PMCID: PMC1665354
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2004.073197
Voltage dependence of ATP-dependent K+ current in rat cardiac myocytes is affected by IK1 and IK(ACh)
Abstract
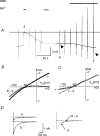
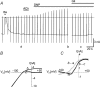
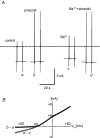
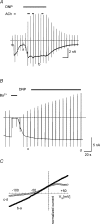
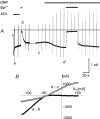
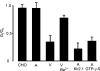
In this study we have investigated the voltage dependence of ATP-dependent K+ current (I(K(ATP))) in atrial and ventricular myocytes from hearts of adult rats and in CHO cells expressing Kir6.2 and SUR2A. The current-voltage relation of 2,4-dinitrophenole (DNP) -induced I(K(ATP)) in atrial myocytes and expressed current in CHO cells was linear in a voltage range between 0 and -100 mV. In ventricular myocytes, the background current-voltage relation of which is dominated by a large constitutive inward rectifier (I(K1)), the slope conductance of I(K(ATP)) was reduced at membrane potentials negative to E(K) (around -50 mV), resulting in an outwardly rectifying I-V relation. Overexpression of Kir2.1 by adenoviral gene transfer, a subunit contributing to I(K1) channels, in atrial myocytes resulted in a large I(K1)-like background current. The I-V relation of I(K(ATP)) in these cells showed a reduced slope conductance negative to E(K) similar to ventricular myocytes. In atrial myocytes with an increased background inward-rectifier current through Kir3.1/Kir3.4 channels (I(K(ACh))), irreversibly activated by intracellular loading with GTP-gamma-S, the I-V relation of I(K(ATP)) showed a reduced slope negative to E(K), as in ventricular myocytes and atrial myocytes overexpressing Kir2.1. It is concluded that the voltage dependencies of membrane currents are not only dependent on the molecular composition of the charge-carrying channel complexes but can be affected by the activity of other ion channel species. We suggest that the interference between inward I(K(ATP)) and other inward rectifier currents in cardiac myocytes reflects steady-state changes in K+ driving force due to inward K+ current.
Figures
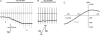


Similar articles
-
Acute desensitization of GIRK current in rat atrial myocytes is related to K+ current flow.J Physiol. 2004 Dec 1;561(Pt 2):471-83. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2004.072462. Epub 2004 Sep 30. J Physiol. 2004. PMID: 15459243 Free PMC article.
-
A key role for the subunit SUR2B in the preferential activation of vascular KATP channels by isoflurane.Br J Pharmacol. 2006 Nov;149(5):573-80. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706891. Epub 2006 Sep 25. Br J Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 17001304 Free PMC article.
-
SUR2A C-terminal fragments reduce KATP currents and ischaemic tolerance of rat cardiac myocytes.J Physiol. 2004 Jun 15;557(Pt 3):785-94. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2004.061655. Epub 2004 Mar 12. J Physiol. 2004. PMID: 15020694 Free PMC article.
-
The inward rectifier current (IK1) controls cardiac excitability and is involved in arrhythmogenesis.Heart Rhythm. 2005 Mar;2(3):316-24. doi: 10.1016/j.hrthm.2004.11.012. Heart Rhythm. 2005. PMID: 15851327 Review.
-
Physiological role of inward rectifier K(+) channels in vascular smooth muscle cells.Pflugers Arch. 2008 Oct;457(1):137-47. doi: 10.1007/s00424-008-0512-7. Epub 2008 Apr 25. Pflugers Arch. 2008. PMID: 18437413 Review.
Cited by
-
Generation of a constitutive Na+-dependent inward-rectifier current in rat adult atrial myocytes by overexpression of Kir3.4.J Physiol. 2007 Nov 15;585(Pt 1):3-13. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2007.140772. Epub 2007 Sep 20. J Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17884923 Free PMC article.
-
Galphai3 primes the G protein-activated K+ channels for activation by coexpressed Gbetagamma in intact Xenopus oocytes.J Physiol. 2007 May 15;581(Pt 1):17-32. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2006.125864. Epub 2007 Feb 8. J Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17289785 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of dihydrolipoyl succinyltransferase (DLST) leads to reduced resting heart rate in the zebrafish.Basic Res Cardiol. 2015 Mar;110(2):14. doi: 10.1007/s00395-015-0468-7. Epub 2015 Feb 20. Basic Res Cardiol. 2015. PMID: 25697682 Free PMC article.
-
Acute desensitization of GIRK current in rat atrial myocytes is related to K+ current flow.J Physiol. 2004 Dec 1;561(Pt 2):471-83. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2004.072462. Epub 2004 Sep 30. J Physiol. 2004. PMID: 15459243 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of 2,5-di-(tert-butyl)-1,4-benzohydroquinone (TBQ) on intracellular Ca2+ handling in rat ventricular myocytes.Cell Calcium. 2015 Aug;58(2):208-14. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2015.05.002. Epub 2015 May 29. Cell Calcium. 2015. PMID: 26120055 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aguilar-Bryan L, Clement JP, Gonzalez G, Kunjilwar K, Babenko A, Bryan J. Toward understanding the assembly and structure of KATP channels. Physiol Rev. 1998;78:227–245. - PubMed
-
- Bender K, Wellner-Kienitz M-C, Inanobe A, Meyer T, Kurachi Y, Pott L. Overexpression of monomeric and multimeric GIRK4 subunits in rat atrial myocytes removes fast desentitization and reduces inward rectification of muscarinic K+ current (IK(ACh)) J Biol Chem. 2001;276:28873–28880. - PubMed
-
- Bielen FV, Glitsch HG, Verdonck F. Changes of the subsarcolemmal Na+ concentration in internally perfused cardiac cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991;1065:269–271. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

