Arabidopsis seedling growth response and recovery to ethylene. A kinetic analysis
- PMID: 15466220
- PMCID: PMC523353
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.104.050369
Arabidopsis seedling growth response and recovery to ethylene. A kinetic analysis
Abstract
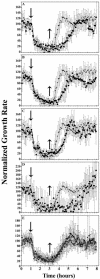
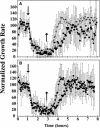
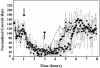
Responses to the plant hormone ethylene are mediated by a family of five receptors in Arabidopsis that act in the absence of ethylene as negative regulators of response pathways. In this study, we examined the rapid kinetics of growth inhibition by ethylene and growth recovery after ethylene withdrawal in hypocotyls of etiolated seedlings of wild-type and ethylene receptor-deficient Arabidopsis lines. This analysis revealed that there are two phases to growth inhibition by ethylene in wild type: a rapid phase followed by a prolonged, slower phase. Full recovery of growth occurs approximately 90 min after ethylene removal. None of the receptor null mutations tested had a measurable effect on the two phases of growth inhibition. However, loss-of-function mutations in ETR1, ETR2, and EIN4 significantly prolonged the time for recovery of growth rate after ethylene was removed. Plants with an etr1-6;etr2-3;ein4-4 triple loss-of-function mutation took longer to recover than any of the single mutants, while the ers1;ers2 double mutant had no effect on recovery rate, suggesting that receiver domains play a role in recovery. Transformation of the ers1-2;etr1-7 double mutant with wild-type genomic ETR1 rescued the slow recovery phenotype, while a His kinase-inactivated ETR1 construct did not. To account for the rapid recovery from growth inhibition, a model in which clustered receptors act cooperatively is proposed.
Figures



References
-
- Alonso JM, Hirayama T, Roman G, Nourizadeh S, Ecker JR (1999) EIN2, a bifunctional transducer of ethylene and stress responses in Arabidopsis. Science 284: 2148–2152 - PubMed
-
- Bleecker AB, Estelle MA, Somerville C, Kende H (1988) Insensitivity to ethylene conferred by a dominant mutation in Arabidopsis thaliana. Science 241: 1086–1089 - PubMed
-
- Bray D, Levin MD, Morton-Firth CJ (1998) Receptor clustering as a cellular mechanism to control sensitivity. Nature 393: 85–88 - PubMed
-
- Blankenship SM, Dole JM (2003) 1-Methylcyclopropene: a review. Postharvest Biol Tec 28: 1–25
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

