Method for combining information from white matter fiber tracking and gray matter parcellation
- PMID: 15466325
- PMCID: PMC2813857
Method for combining information from white matter fiber tracking and gray matter parcellation
Abstract
We introduce a method for combining fiber tracking from diffusion-tensor (DT) imaging with cortical gray matter parcellation from structural high-spatial-resolution 3D spoiled gradient-recalled acquisition in the steady state images. We applied this method to a tumor case to determine the impact of the tumor on white matter architecture. We conclude that this new method for combining structural and DT imaging data is useful for understanding cortical connectivity and the localization of fiber tracts and their relationship with cortical anatomy and brain abnormalities.
Figures






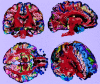
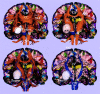
References
-
- Basser PJ, Mattiello J, LeBihan D. Estimation of the effective self-diffusion tensor from the NMR spin echo. J Magn Reson B 1994;103:247–254 - PubMed
-
- Basser PJ. Fiber-tractography via diffusion tensor MRI (DT-MRI). In: Proceedings of the 6th Annual Meeting ISMRM, Sydney, Australia,1998;1226
-
- Westin CF, Maier SE, Mamata H, et al. Processing and visualization for diffusion tensor MRI. Med Image Anal 2002;6:93–108 - PubMed
-
- Talos I-F, O’Donnell L, Westin C-F, et al. Diffusion tensor and functional MRI fusion with anatomical MRI for image-guided neurosurgery. In: Ellis RE, Peters TM, eds. Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI’03). Montreal, Canada: Springer Verlag,2003;407–415
-
- Gudbjartsson H, Maier SE, Mulkern RV, et al. Line scan diffusion imaging. Magn Reson Med 1996;36:509–519 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
