Successful revascularization of acute carotid stent thrombosis by facilitated thrombolysis
- PMID: 15466343
- PMCID: PMC7975469
Successful revascularization of acute carotid stent thrombosis by facilitated thrombolysis
Abstract
A 64-year-old woman undergoing protected carotid artery stent placement developed acute stent thrombosis despite pretreatment with combined antiplatelet therapy. A reduced dose of recombinant tissue plasminogen activator and a half-dose bolus of abciximab were administered intra-arterially via superselective catherization followed by systemic intravenous infusion of abciximab for 12 hours. Control angiography showed complete restoration of blood flow paralleled by neurologic improvement.
Figures
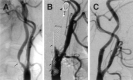
References
-
- Moussa I, Gishel N, Lawrence E, et al. Clopidogrel may enhance the clinical efficacy of carotid artery stent implantation: the EMILY registry. Stroke 2000;31:299
-
- Wholey MH, Wholey M. Current status in cervical carotid artery stent placement. J Cardiovasc Surg 2003;44:331–339 - PubMed
-
- Marciniak SJ Jr, Mascelli MA, Furman MI, et al. An additional mechanism of action of abciximab: dispersal of newly formed platelet aggregates. Thromb Haemost 2002;87:1020–1025 - PubMed
-
- Luciardi H, Berman S, Muntaner J, et al. Facilitated thrombolysis: dethrombosis? Clin Appl Thromb Hemost 2002;8:133–138 - PubMed
-
- North American Symptomatic Carotid Endarterectomy Collaborators. Beneficial effect of carotid endarterectomy in symptomatic patients with high-grade carotid stenosis. N Engl J Med 1991;325:445–453 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
