Impairment of the low-affinity state beta1-adrenoceptor-induced relaxation in spontaneously hypertensive rats
- PMID: 15466443
- PMCID: PMC1575435
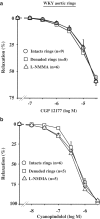
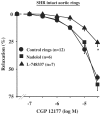
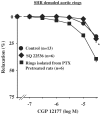
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705990
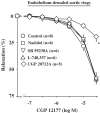
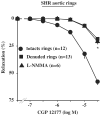
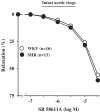
Impairment of the low-affinity state beta1-adrenoceptor-induced relaxation in spontaneously hypertensive rats
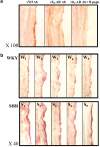
Abstract
1 In hypertension, a decrease of the vascular beta-adrenergic relaxation has been described. However, the specific involvement of each beta-adrenoceptor (beta-AR) subtype, in particular the low-affinity state of beta1-AR, has not yet been evaluated. We investigated whether the low-affinity state of beta1-AR-induced relaxation was impaired in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats (SHR). 2 The relaxant responses to CGP 12177 and cyanopindolol, low-affinity state beta1-AR agonists (with beta1-/beta2-AR antagonistic and partial beta3-AR agonistic properties) were evaluated on thoracic aortic rings isolated from 12-weeks-old Wistar Kyoto rats (WKY) and SHR. 3 In WKY, CGP 12177 and cyanopindolol produced an endothelium and nitric oxide (NO)-independent relaxation. CGP 12177-induced endothelium-independent relaxation was not modified either by beta1-, beta2-AR (nadolol) or beta3-AR (L-748337 or SR 59230A) antagonists but was significantly reduced by high concentrations of CGP 20712A (P<0.05). This relaxation was also reduced by adenylyl cyclase inhibitors, SQ 22536 or MDL 12330A. 4 In SHR, CGP 12177 produced mainly an endothelium and NO-dependent relaxation. This effect was not modified by nadolol, but was strongly reduced by beta3-AR blockade. Endothelium-independent relaxation to CGP 12177 was not altered by adenylyl cyclase inhibition, but was amplified in preparations from pertussis toxin-pretreated SHR. 5 The immunohistochemical analysis revealed an upregulation of beta3-AR in the endothelial layer of SHR aorta, whereas the beta3-AR-induced relaxation was not modified. 6 In conclusion, we demonstrated an impaired low-affinity state of the beta1-AR-induced relaxation and an upregulation of the beta3-AR in hypertension. Some clinical implications of those findings are discussed.
Figures

Comment in
-
Do low-affinity states of beta-adrenoceptors have roles in physiology and medicine?Br J Pharmacol. 2004 Nov;143(5):517-8. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705991. Br J Pharmacol. 2004. PMID: 15514247 Free PMC article.
References
-
- ANAND-SRIVASTAVA M.B. G-proteins and adenylyl cyclase signalling in hypertention. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 1996;157:163–170. - PubMed
-
- ARRIBAS S., MARIN J., PONTE A., BALFAGON G., SALAICES M. Norepinephrine-induced relaxations in rat aorta mediated by endothelial beta adrenoceptors. Impairment by ageing and hypertension. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1994;270:520–527. - PubMed
-
- BAKER J.G., HALL I.P., HILL S.J. Agonist actions of ‘β-blockers' provide evidence for two agonist activation sites or conformations of the human β1-adrenoceptor. Mol. Pharmacol. 2003;63:1312–1321. - PubMed
-
- BOONEN H.C., DAEMEN M.J., EERDMANS P.H., FAZZI G.E., VAN KLEEF E.M., SCHIFFERS P.M., DE MEY J.G. Mesenteric small artery changes after vasoconstrictor infusion in young rats. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 1993;22:388–395. - PubMed
-
- BORKOWSKI K.R., GROS R., SCHNEIDER H. Vascular beta-adrenoceptor-mediated responses in hypertension and ageing in rats. J. Auton. Pharmacol. 1992;12:389–401. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

