Small interfering RNA targeting Fas protects mice against renal ischemia-reperfusion injury
- PMID: 15466709
- PMCID: PMC522049
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0406421101
Small interfering RNA targeting Fas protects mice against renal ischemia-reperfusion injury
Abstract
Fas-mediated apoptosis has been suggested to contribute to tubular cell death after renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. Here we investigate whether small interfering RNA (siRNA) duplexes targeting Fas protect mice from acute renal failure after clamping of the renal artery. Renal ischemia-reperfusion injury was induced by clamping the renal vein and artery for 15 or 35 min. Mice were treated before or after ischemia with siRNA targeting Fas or a control gene, administered by hydrodynamic injection, low-volume renal vein injection, or both. Treated mice were evaluated for renal Fas protein and mRNA expression, tissue histopathology, and apoptosis by terminal deoxynucleotidyltransferase-mediated dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) staining. Blood urea nitrogen and survival were monitored in mice in which the contralateral kidney had been removed. A single hydrodynamic injection of Fas siRNA reduced Fas mRNA and protein expression in the kidney 4-fold. Kidneys from mice that received Fas siRNA two days earlier had substantially less renal tubular apoptosis by TUNEL staining and less tubular atrophy and hyaline damage. Whereas 90% of mice pretreated with saline or GFP siRNA died, only 20% of Fas-siRNA-pretreated animals died. The same survival advantage was provided by a single low-volume Fas siRNA injection into the renal vein. Moreover, postischemic injection through the renal vein protected 38% of mice from death. This study confirms the importance of Fas-mediated apoptosis in renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. Silencing Fas by systemic or local catheterization holds therapeutic promise to limit ischemia-reperfusion injury.
Figures

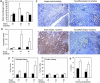
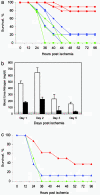
References
-
- Nogae, S., Miyazaki, M., Kobayashi, N., Saito, T., Abe, K., Saito, H., Nakane, P. K., Nakanishi, Y. & Koji, T. (1998) J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 9, 620-631. - PubMed
-
- Paschen, W. (2003) J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 23, 773-779. - PubMed
-
- Martin-Villalba, A., Hahne, M., Kleber, S., Vogel, J., Falk, W., Schenkel, J. & Krammer, P. H. (2001) Cell Death Differ. 8, 679-686. - PubMed
-
- Castaneda, M. P., Swiatecka-Urban, A., Mitsnefes, M. M., Feuerstein, D., Kaskel, F. J., Tellis, V. & Devarajan, P. (2003) Transplantation 76, 50-54. - PubMed
-
- Lee, P., Sata, M., Lefer, D. J., Factor, S. M., Walsh, K. & Kitsis, R. N. (2003) Am. J. Physiol. 284, H456-H463. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

