Significance of MDR1 and multiple drug resistance in refractory human epileptic brain
- PMID: 15473912
- PMCID: PMC524356
- DOI: 10.1186/1741-7015-2-37
Significance of MDR1 and multiple drug resistance in refractory human epileptic brain
Abstract
Background: The multiple drug resistance protein (MDR1/P-glycoprotein) is overexpressed in glia and blood-brain barrier (BBB) endothelium in drug refractory human epileptic tissue. Since various antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) can act as substrates for MDR1, the enhanced expression/function of this protein may increase their active extrusion from the brain, resulting in decreased responsiveness to AEDs.
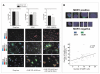
Methods: Human drug resistant epileptic brain tissues were collected after surgical resection. Astrocyte cell cultures were established from these tissues, and commercially available normal human astrocytes were used as controls. Uptake of fluorescent doxorubicin and radioactive-labeled Phenytoin was measured in the two cell populations, and the effect of MDR1 blockers was evaluated. Frozen human epileptic brain tissue slices were double immunostained to locate MDR1 in neurons and glia. Other slices were exposed to toxic concentrations of Phenytoin to study cell viability in the presence or absence of a specific MDR1 blocker.
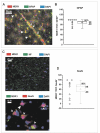
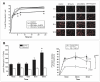
Results: MDR1 was overexpressed in blood vessels, astrocytes and neurons in human epileptic drug-resistant brain. In addition, MDR1-mediated cellular drug extrusion was increased in human 'epileptic' astrocytes compared to 'normal' ones. Concomitantly, cell viability in the presence of cytotoxic compounds was increased.
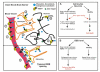
Conclusions: Overexpression of MDR1 in different cell types in drug-resistant epileptic human brain leads to functional alterations, not all of which are linked to drug pharmacokinetics. In particular, the modulation of glioneuronal MDR1 function in epileptic brain in the presence of toxic concentrations of xenobiotics may constitute a novel cytoprotective mechanism.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Drug resistance in epilepsy: expression of drug resistance proteins in common causes of refractory epilepsy.Brain. 2002 Jan;125(Pt 1):22-31. doi: 10.1093/brain/awf002. Brain. 2002. PMID: 11834590
-
MDR1 gene expression in brain of patients with medically intractable epilepsy.Epilepsia. 1995 Jan;36(1):1-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1995.tb01657.x. Epilepsia. 1995. PMID: 8001500
-
Vascular and parenchymal mechanisms in multiple drug resistance: a lesson from human epilepsy.Curr Drug Targets. 2003 May;4(4):297-304. doi: 10.2174/1389450033491109. Curr Drug Targets. 2003. PMID: 12699350 Review.
-
Development of a humanized in vitro blood-brain barrier model to screen for brain penetration of antiepileptic drugs.Epilepsia. 2007 Mar;48(3):505-16. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1167.2006.00960.x. Epub 2007 Feb 22. Epilepsia. 2007. PMID: 17326793
-
ABC transporters during epilepsy and mechanisms underlying multidrug resistance in refractory epilepsy.Epilepsia. 2007;48 Suppl 5:140-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1167.2007.01302.x. Epilepsia. 2007. PMID: 17910594 Review.
Cited by
-
Transcranial Focal Electric Stimulation Avoids P-Glycoprotein Over-Expression during Electrical Amygdala Kindling and Delays Epileptogenesis in Rats.Life (Basel). 2023 May 31;13(6):1294. doi: 10.3390/life13061294. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37374077 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic targeting of senescent cells in the CNS.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2024 Nov;23(11):817-837. doi: 10.1038/s41573-024-01033-z. Epub 2024 Sep 30. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2024. PMID: 39349637 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of multidrug transporters in neurotherapeutics.Ann Indian Acad Neurol. 2009 Apr;12(2):89-98. doi: 10.4103/0972-2327.53076. Ann Indian Acad Neurol. 2009. PMID: 20142853 Free PMC article.
-
Aberrant expression of miR-153 is associated with overexpression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α in refractory epilepsy.Sci Rep. 2016 Aug 24;6:32091. doi: 10.1038/srep32091. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27554040 Free PMC article.
-
What non-neuronal mechanisms should be studied to understand epileptic seizures?Adv Exp Med Biol. 2014;813:253-64. doi: 10.1007/978-94-017-8914-1_20. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2014. PMID: 25012382 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abbott NJ, Khan EU, Rollinson C, Reichel A, Janigro D, Dombrowski S, et al. Drug resistance in epilepsy: the role of the blood-brain barrier. In: Ling V, editor. In Mechanisms of drug resistance in epilepsy: lessons from oncology. Chichester, UK: John Wiley; 2001. pp. 38–47. - PubMed
-
- Aronica E, Gorter JA, Ramkema M, Redeker S, Ozbas-Gercerer F, van Vliet EA, et al. Expression and cellular distribution of multidrug resistance-related proteins in the hippocampus of patients with mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsia. 2004;45:441–451. doi: 10.1111/j.0013-9580.2004.57703.x. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

