Stem cell expression of the AML1/ETO fusion protein induces a myeloproliferative disorder in mice
- PMID: 15477599
- PMCID: PMC524043
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0400751101
Stem cell expression of the AML1/ETO fusion protein induces a myeloproliferative disorder in mice
Abstract
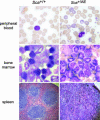
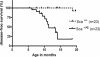
The t(8;21)(q22;q22) translocation, present in 10-15% of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cases, generates the AML1/ETO fusion protein. To study the role of AML1/ETO in the pathogenesis of AML, we used the Ly6A locus that encodes the well characterized hematopoietic stem cell marker, Sca1, to target expression of AML1/ETO to the hematopoietic stem cell compartment in mice. Whereas germ-line expression of AML1/ETO from the AML1 promoter results in embryonic lethality, heterozygous Sca1(+/AML1-ETO ires EGFP) (abbreviated Sca(+/AE)) mutant mice are born in Mendelian ratios with no apparent abnormalities in growth or fertility. Hematopoietic cells from Sca(+/AE) mice have markedly extended survival in vitro and increasing myeloid clonogenic progenitor output over time. Sca(+/AE) mice develop a spontaneous myeloproliferative disorder with a latency of 6 months and a penetrance of 82% at 14 months. These results reinforce the notion that the phenotype of murine transgenic models of human leukemia is critically dependent on the cellular compartment targeted by the transgene. This model should provide a useful platform to analyze the effect of AML1/ETO on hematopoiesis and its potential cooperation with other mutations in the pathogenesis of leukemia.
Figures



References
-
- Downing, J. R. (1999) Br. J. Haematol. 106, 296-308. - PubMed
-
- Nucifora, G. & Rowley, J. D. (1995) Blood 86, 1-14. - PubMed
-
- Okuda, T., van Deursen, J., Hiebert, S. W., Grosveld, G. & Downing, J. R. (1996) Cell 84, 321-330. - PubMed
-
- Wang, Q., Stacy, T., Miller, J. D., Lewis, A. F., Gu, T. L., Huang, X., Bushweller, J. H., Bories, J. C., Alt, F. W., Ryan, G., et al. (1996) Cell 87, 697-708. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

