Phase I clinical trial and pharmacokinetic evaluation of NK911, a micelle-encapsulated doxorubicin
- PMID: 15477860
- PMCID: PMC2410050
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6602204
Phase I clinical trial and pharmacokinetic evaluation of NK911, a micelle-encapsulated doxorubicin
Abstract
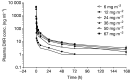
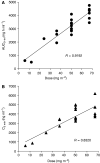
NK911 is a novel supramolecular nanocarrier designed for the enhanced delivery of doxorubicin (DXR) and is one of the successful polymer micelle systems to exhibit an efficient accumulation in solid tumours in mice. The purpose of this study was to define the maximum-tolerated dose (MTD) and dose-limiting toxicities (DLTs) of NK911 and to evaluate its pharmacokinetic profile in man. NK911 was given intravenously to patients with solid tumours every 3 weeks using an infusion pump at a rate of 10 mg DXR equivalent min(-1). The starting dose was 6 mg DXR equivalent m(-2), and the dose was escalated according to the accelerated titration method. A total of 23 patients participated in this study. Neutropenia was the predominant haematological toxicity, and grade 3 or 4 neutropenia was observed at doses of 50 and 67 mg m(-2). Common nonhaematological toxicities were mild alopecia, stomatitis, and anorexia. In the dose identification part of the study, DLTs were observed at a dose of 67 mg m(-2) (grade 4 neutropenia lasting more than 5 days). Thus, this dosage level was determined to be the MTD. Infusion-related reactions were not observed in any cases. The C(5 min) and area under the concentration curve parameters of NK911 exhibited dose-dependent characteristics. Among the 23 patients, a partial response was obtained in one patient with metastatic pancreatic cancer. NK911 was well tolerated and produced only moderate nausea and vomiting at myelosuppressive dosages. The recommended phase II dose was determined to be 50 mg m(-2) every 3 weeks.
Figures

References
-
- Gabizon A, Catane R, Uziely B, Kaufman B, Safra T, Cohen R, Martin F, Huang A, Barenholz Y (1994) Prolonged circulation time and enhanced accumulation in malignant exudates of doxorubicin encapsulated in polyethylene-glycol coated liposomes. Cancer Res 54: 987–992 - PubMed
-
- Gordon AN, Fleagle JT, Guthrie D, Parkin DE, Gore ME, Lacave AJ (2001) Recurrent epithelial ovarian carcinoma: a randomized phase III study of pegylated liposomal doxorubicin vs topotecan. J Clin Oncol 19: 3312–3322 - PubMed
-
- Maeda H, Wu J, Sawa T, Matsumura Y, Hori K (2000) Tumor vascular permeability and the EPR effect in macromolecular therapeutics: a review. J Control Release 65: 271–284 - PubMed
-
- Matsumura Y, Maeda H (1986) A new concept for macromolecular therapeutics in cancer chemotherapy: mechanism of tumoritropic accumulation of proteins and the antitumor agent smancs. Cancer Res 46: 6387–6392 - PubMed
-
- Mross K, Maessen P, van der Vijgh WJ, Gall H, Boven E, Pinedo HM (1988) Pharmacokinetics and metabolism of epidoxorubicin and doxorubicin in humans. J Clin Oncol 6: 517–526 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

