The C-mer gene is induced by Epstein-Barr virus immediate-early protein BRLF1
- PMID: 15479819
- PMCID: PMC523243
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.78.21.11778-11785.2004
The C-mer gene is induced by Epstein-Barr virus immediate-early protein BRLF1
Abstract
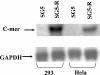
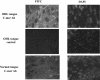
BRLF1 (R) is one of two Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) immediate-early proteins that mediate the switch from the latent to the lytic form of viral replication. In this report, we show that R induces expression of the cellular C-mer gene in a variety of cell lines. C-mer expression was detected in lymphoblastoid cells immortalized with wild-type EBV but not in lymphoblastoid cells immortalized with an EBV that had BRLF1 deleted. Oral hairy leukoplakia tongue tissue, which contains the lytic form of EBV replication, also has enhanced C-mer expression. C-mer is a receptor tyrosine kinase activated by the ligand Gas6. C-mer is required for phagocytosis of apoptotic debris by monocytes/macrophages and retinal pigment epithelial cells and is capable of producing an antiapoptotic signal. Modulation of the C-mer signal transduction cascade by a variety of different approaches did not alter the ability of R to induce lytic EBV gene transcription. Therefore, C-mer activation may be important for some other aspect of lytic EBV infection.
Figures


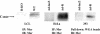

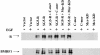

Similar articles
-
Epstein-Barr virus immediate-early protein BRLF1 induces the lytic form of viral replication through a mechanism involving phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase activation.J Virol. 2001 Jul;75(13):6135-42. doi: 10.1128/JVI.75.13.6135-6142.2001. J Virol. 2001. PMID: 11390615 Free PMC article.
-
Fatty acid synthase expression is induced by the Epstein-Barr virus immediate-early protein BRLF1 and is required for lytic viral gene expression.J Virol. 2004 Apr;78(8):4197-206. doi: 10.1128/jvi.78.8.4197-4206.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 15047835 Free PMC article.
-
The BRRF1 early gene of Epstein-Barr virus encodes a transcription factor that enhances induction of lytic infection by BRLF1.J Virol. 2004 May;78(10):4983-92. doi: 10.1128/jvi.78.10.4983-4992.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 15113878 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr virus immediate-early protein BRLF1 interacts with CBP, promoting enhanced BRLF1 transactivation.J Virol. 2001 Jul;75(13):6228-34. doi: 10.1128/JVI.75.13.6228-6234.2001. J Virol. 2001. PMID: 11390628 Free PMC article.
-
Lytic cycle switches of oncogenic human gammaherpesviruses.Adv Cancer Res. 2007;97:81-109. doi: 10.1016/S0065-230X(06)97004-3. Adv Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17419942 Review.
Cited by
-
The TAM family: phosphatidylserine sensing receptor tyrosine kinases gone awry in cancer.Nat Rev Cancer. 2014 Dec;14(12):769-85. doi: 10.1038/nrc3847. Nat Rev Cancer. 2014. PMID: 25568918 Review.
-
Analysis of Ebola Virus Entry Into Macrophages.J Infect Dis. 2015 Oct 1;212 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):S247-57. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiv140. Epub 2015 Apr 14. J Infect Dis. 2015. PMID: 25877552 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr virus lytic infection is required for efficient production of the angiogenesis factor vascular endothelial growth factor in lymphoblastoid cell lines.J Virol. 2005 Nov;79(22):13984-92. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.22.13984-13992.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 16254334 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr virus lytic infection contributes to lymphoproliferative disease in a SCID mouse model.J Virol. 2005 Nov;79(22):13993-4003. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.22.13993-14003.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 16254335 Free PMC article.
-
MERTK in cancer therapy: Targeting the receptor tyrosine kinase in tumor cells and the immune system.Pharmacol Ther. 2020 Sep;213:107577. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2020.107577. Epub 2020 May 14. Pharmacol Ther. 2020. PMID: 32417270 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adamson, A. L., D. Darr, E. Holley-Guthrie, R. A. Johnson, A. Mauser, J. Swenson, and S. Kenney. 2000. Epstein-Barr virus immediate-early proteins BZLF1 and BRLF1 activate the ATF2 transcription factor by increasing the levels of phosphorylated p38 and c-Jun N-terminal kinases. J. Virol. 74:1224-1233. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Camenisch, T. D., B. H. Koller, H. S. Earp, and G. K. Matsushima. 1999. A novel receptor tyrosine kinase, Mer, inhibits TNF-alpha production and lipopolysaccharide-induced endotoxic shock. J. Immunol. 162:3498-3503. - PubMed
-
- Chen, J., K. Carey, and P. J. Godowski. 1997. Identification of Gas6 as a ligand for Mer, a neural cell adhesion molecule related receptor tyrosine kinase implicated in cellular transformation. Oncogene. 14:2033-2039. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

