An intermediate grade of finished genomic sequence suitable for comparative analyses
- PMID: 15479945
- PMCID: PMC525681
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.2648404
An intermediate grade of finished genomic sequence suitable for comparative analyses
Abstract
Although the cost of generating draft-quality genomic sequence continues to decline, refining that sequence by the process of "sequence finishing" remains expensive. Near-perfect finished sequence is an appropriate goal for the human genome and a small set of reference genomes; however, such a high-quality product cannot be cost-justified for large numbers of additional genomes, at least for the foreseeable future. Here we describe the generation and quality of an intermediate grade of finished genomic sequence (termed comparative-grade finished sequence), which is tailored for use in multispecies sequence comparisons. Our analyses indicate that this sequence is very high quality (with the residual gaps and errors mostly falling within repetitive elements) and reflects 99% of the total sequence. Importantly, comparative-grade sequence finishing requires approximately 40-fold less reagents and approximately 10-fold less personnel effort compared to the generation of near-perfect finished sequence, such as that produced for the human genome. Although applied here to finishing sequence derived from individual bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC) clones, one could envision establishing routines for refining sequences emanating from whole-genome shotgun sequencing projects to a similar quality level. Our experience to date demonstrates that comparative-grade sequence finishing represents a practical and affordable option for sequence refinement en route to comparative analyses.
Figures

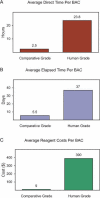
References
-
- Adams, M.D., Celniker, S.E., Holt, R.A., Evans, C.A., Gocayne, J.D., Amanatides, P.G., Scherer, S.E., Li, P.W., Hoskins, R.A., Galle, R.F., et al. 2000. The genome sequence of Drosophila melanogaster. Science 287: 2185-2195. - PubMed
-
- Aparicio, S., Chapman, J., Stupka, E., Putnam, N., Chia, J., Dehal, P., Christoffels, A., Rash, S., Hoon, S., Smit, A., et al. 2002. Whole-genome shotgun assembly and analysis of the genome of Fugu rubripes. Science 297: 1301-1310. - PubMed
-
- Ashurst, J.L. and Collins, J.E. 2003. Gene annotation: Prediction and testing. Annu. Rev. Genomics Hum. Genet. 4: 69-88. - PubMed
-
- Bailey, J.A., Gu, Z., Clark, R.A., Reinert, K., Samonte, R.V., Schwartz, S., Adams, M.D., Myers, E.W., Li, P.W., and Eichler, E.E. 2002. Recent segmental duplications in the human genome. Science 297: 1003-1007. - PubMed
WEB SITE REFERENCES
-
- www.nisc.nih.gov/data; source of Supplemental data and information.
-
- www.nisc.nih.gov; NIH Intramural Sequencing Center (NISC) home page and source of information for the NISC Comparative Sequencing Program.
-
- www.genome.wustl.edu/Overview/finrulesname.php?G16=1; quality specifications for the finished human genome sequence.
-
- www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/HTGS; definitions of different phases of genomic sequence.
-
- www.phrap.org; source of Phred, Phrap, Consed, and Cross_Match software.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
