Nuclear factor-kappaB p65 (RelA) transcription factor is constitutively activated in human colorectal carcinoma tissue
- PMID: 15484295
- PMCID: PMC4572290
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i22.3255
Nuclear factor-kappaB p65 (RelA) transcription factor is constitutively activated in human colorectal carcinoma tissue
Abstract
Aim: Activation of transcription factor nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) has been shown to play a role in cell proliferation, apoptosis, cytokine production, and oncogenesis. The purpose of this study was to determine whether NF-kappaB was constitutively activated in human colorectal tumor tissues and, if so, to determine the role of NF-kappaB in colorectal tumorigenesis, and furthermore, to determine the association of RelA expression with tumor cell apoptosis and the expression of Bcl-2 and Bcl-x(L).
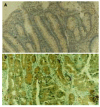
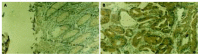
Methods: Paraffin sections of normal epithelial, adenomatous and adenocarcinoma tissues were analysed immunohistochemically for expression of RelA, Bcl-2 and Bcl-x(L) proteins. Electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA) was used to confirm the increased nuclear translocation of RelA in colorectal tumor tissues. The mRNA expressions of Bcl-2 and Bcl-x(L) were determined by reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) analysis. Apoptotic cells were detected by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated deoxyuridine triphosphate fluorescence nick end labeling (TUNEL) method.
Results: The activity of NF-kappaB was significantly higher in adenocarcinoma tissue in comparison with that in adenomatous and normal epithelial tissues. The apoptotic index (AI) significantly decreased in the transition from adenoma to adenocarcinoma. Meanwhile, the expressions of Bcl-2 and Bcl-x(L) protein and their mRNAs were significantly higher in adenocarcinoma tissues than that in adenomatous and normal epithelial tissues.
Conclusion: NF-kappaB may inhibit apoptosis via enhancing the expression of the apoptosis genes Bcl-2 and Bcl-x(L). And the increased expression of RelA/nuclear factor-kappaB plays an important role in the pathogenesis of colorectal carcinoma.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Increased expression of RelA/nuclear factor-kappa B protein correlates with colorectal tumorigenesis.Oncology. 2003;65(1):37-45. doi: 10.1159/000071203. Oncology. 2003. PMID: 12837981
-
Nuclear factor-kappa B regulates cyclooxygenase-2 expression and cell proliferation in human colorectal carcinoma tissue.Eksp Onkol. 2004 Mar;26(1):40-7. Eksp Onkol. 2004. PMID: 15112579
-
[Immunohistochemical analysis of nuclear factor, p38, and cyclin D1 proteins in premalignant lesions and carcinomas of the colorectal mucosa].Korean J Gastroenterol. 2008 Dec;52(6):359-67. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2008. PMID: 19096253 Korean.
-
Transcriptional regulation of the BCL-X gene by NF-kappaB is an element of hypoxic responses in the rat brain.Neurochem Res. 2001 Jun;26(6):647-59. doi: 10.1023/a:1010987220034. Neurochem Res. 2001. PMID: 11519724 Review.
-
Cytokines, NF-kappaB, microenvironment, intestinal inflammation and cancer.Cancer Treat Res. 2006;130:67-87. doi: 10.1007/0-387-26283-0_3. Cancer Treat Res. 2006. PMID: 16610703 Review.
Cited by
-
Cellular and molecular events in colorectal cancer: biological mechanisms, cell death pathways, drug resistance and signalling network interactions.Discov Oncol. 2024 Jul 20;15(1):294. doi: 10.1007/s12672-024-01163-1. Discov Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39031216 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IL-17/miR-192/IL-17Rs regulatory feedback loop facilitates multiple myeloma progression.PLoS One. 2014 Dec 9;9(12):e114647. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0114647. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25489847 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular profile of colorectal cancer in Indonesia: is there another pathway?Gastroenterol Hepatol Bed Bench. 2012 Spring;5(2):71-8. Gastroenterol Hepatol Bed Bench. 2012. PMID: 24834203 Free PMC article. Review.
-
(E)-4-(3-(3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)allyl)-2-methoxyphenol inhibits growth of colon tumors in mice.Oncotarget. 2015 Dec 8;6(39):41929-43. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.5861. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26474284 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Knockout of Fatty Acid Amide Hydrolase Ameliorates Cisplatin-Induced Nephropathy in Mice.Mol Pharmacol. 2023 Apr;103(4):230-240. doi: 10.1124/molpharm.122.000618. Epub 2023 Jan 26. Mol Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36702548 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ghosh S, May MJ, Kopp EB. NF-kappa B and Rel proteins: evolutionarily conserved mediators of immune responses. Annu Rev Immunol. 1998;16:225–260. - PubMed
-
- Micheau O, Tschopp J. Induction of TNF receptor I-mediated apoptosis via two sequential signaling complexes. Cell. 2003;114:181–190. - PubMed
-
- Siebenlist U, Franzoso G, Brown K. Structure, regulation and function of NF-kappa B. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1994;10:405–455. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

